Node - AI Agent
1. Overview
The AI Agent node is an intelligent decision-making node within a workflow. It equips workflows with natural language understanding and autonomous reasoning capabilities.
By leveraging large language models (LLMs), the AI Agent node can execute tasks such as data querying, information summarization, and report generation—based on context data, tool configurations, and prompts—enabling workflows to handle processes intelligently.
2. Common Use Cases
Typical use cases for AI Agent nodes include:
-
Smart Summarization: Generate summaries or conclusions based on upstream node outputs.
-
Intelligent Analysis: Analyze content within attachments or generate structured reports.
-
Automated Data Queries & Notifications: Automatically trigger business tools based on natural language prompts, such as querying records or sending internal messages.
-
Multi-Turn Dialogue: Power smart responses in ChatBot scenarios with memory of prior exchanges.
3. Expected Outcome
The following example illustrates the AI Agent node in a customer management workflow.
When a high-value customer in a worksheet has not been followed up for over 7 days, the AI Agent will:
-
Invoke a record query tool to retrieve relevant customer information and communication history.
-
Generate a reminder message based on the data.
-
Trigger an email-sending tool to notify the responsible sales representative.
Demonstration Scenario:
System detects an overdue follow-up → AI Agent generates a reminder message → Email is automatically sent to the responsible sales representative.
4. Node Configuration
Add an AI Agent Node
In the workflow editor, click the "+" button to add an AI Agent node.
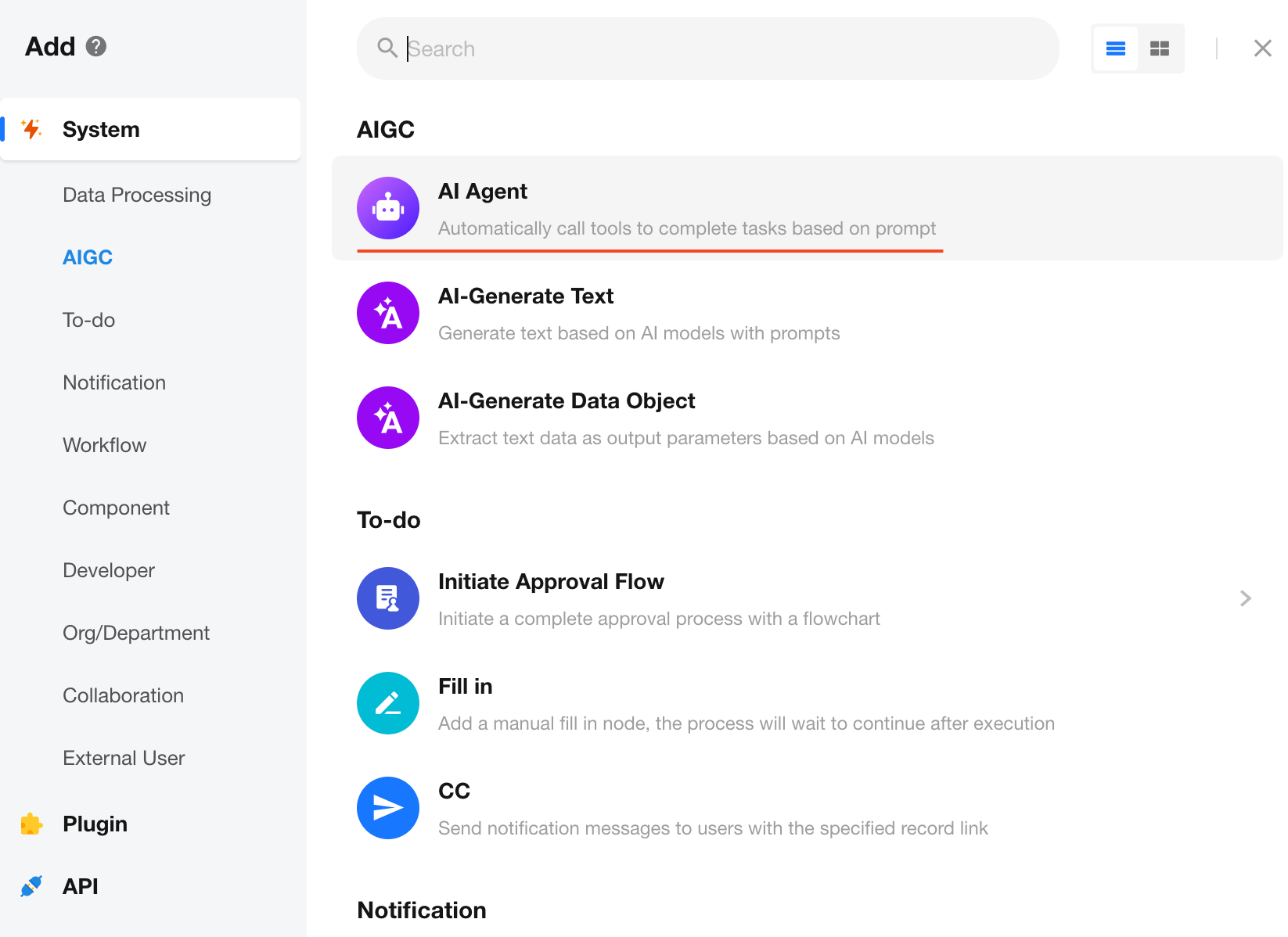
Model Settings
You can choose from a range of large language models (LLMs) to perform the task.
Steps:
- Select a model under the Model dropdown (e.g., DeepSeek-V3, Qwen-Max, GPT-5, GPT-4o, etc.);
- (Optional) Configure model parameters to fine-tune output behavior;
- Save the configuration to activate the changes.
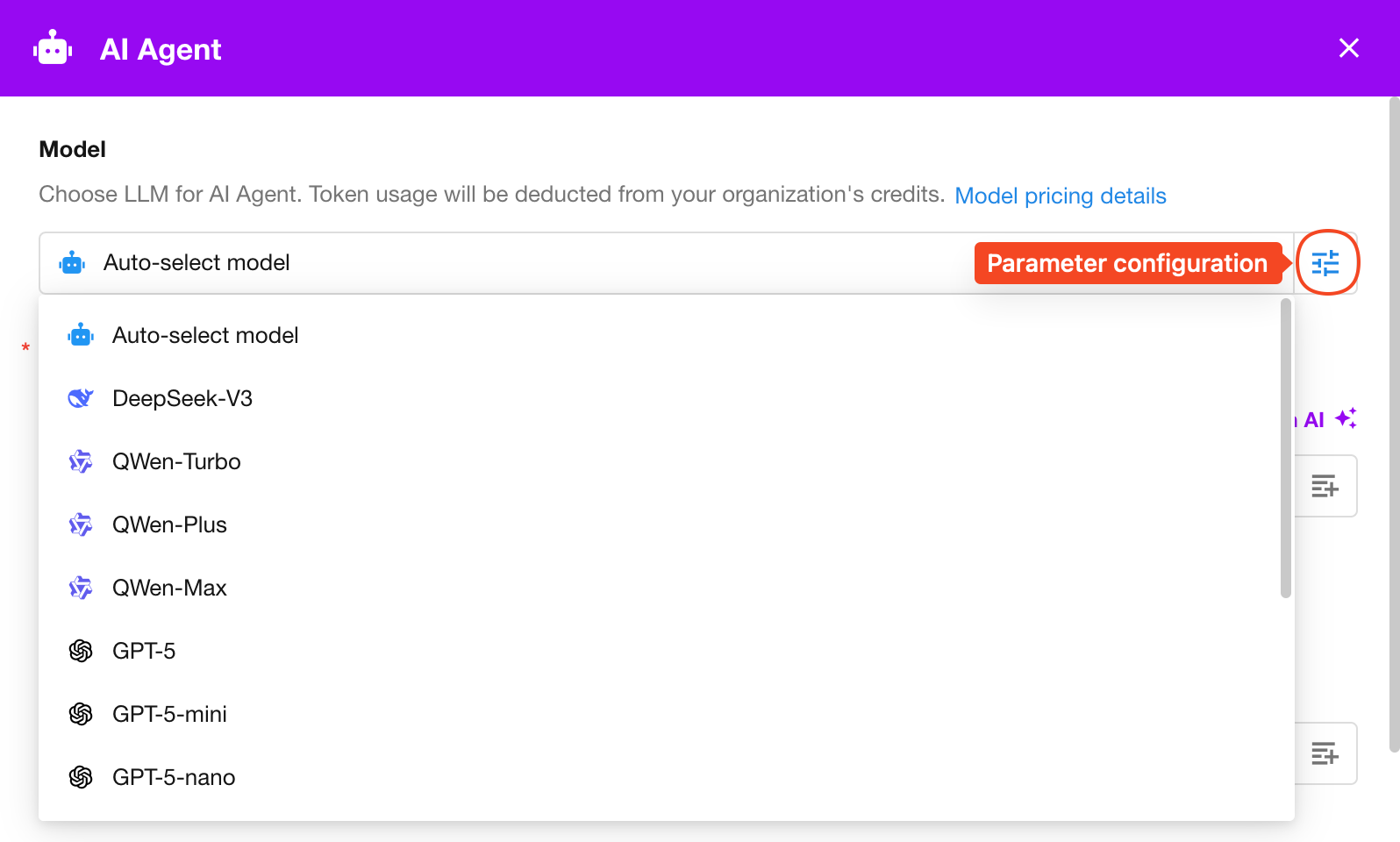
Prompt
The prompt defines the Agent’s role and goal, helping the model understand the task context.
Example:
You are a Customer Management Assistant. Your task is to generate and send reminders based on customer data. When a high-value customer in the customer management worksheet has not been followed up for more than 7 days, you must generate a reminder email and send it to the corresponding sales representative.
Recommendations:
-
Clearly define the task objective (e.g., “generate explanation,” “analyze data”);
-
Avoid vague phrases (e.g., “check this out”);
-
Use variables to reference data from upstream nodes, such as customer name, last follow-up date, etc.
File Link
File links allow you to reference file-type fields from previous nodes.
The AI Agent will treat the file content as context for analysis, summarization, or explanation generation.
💡 Notes:
- Files can come from user uploads or file fields in worksheets.
- This feature may incur higher usage costs.
- Image files require a model with image recognition capabilities.
- Document files are processed by the document analysis service (0.72 credits per document).
Memory Turns
In ChatBot workflows, the AI Agent node supports multi-turn memory to maintain conversation context across turns.
Tool Configuration
With proper tool configuration, the Agent can automatically execute tasks such as data queries, statistics, record updates, and notification delivery — all through natural language commands.
In enterprise-grade systems, data security and access control are crucial. HAP provides two levels of access control for AI Agent nodes: Worksheet Scope and Query Filters. These settings ensure that while enabling intelligent automation, the Agent’s data access boundaries remain clearly defined.
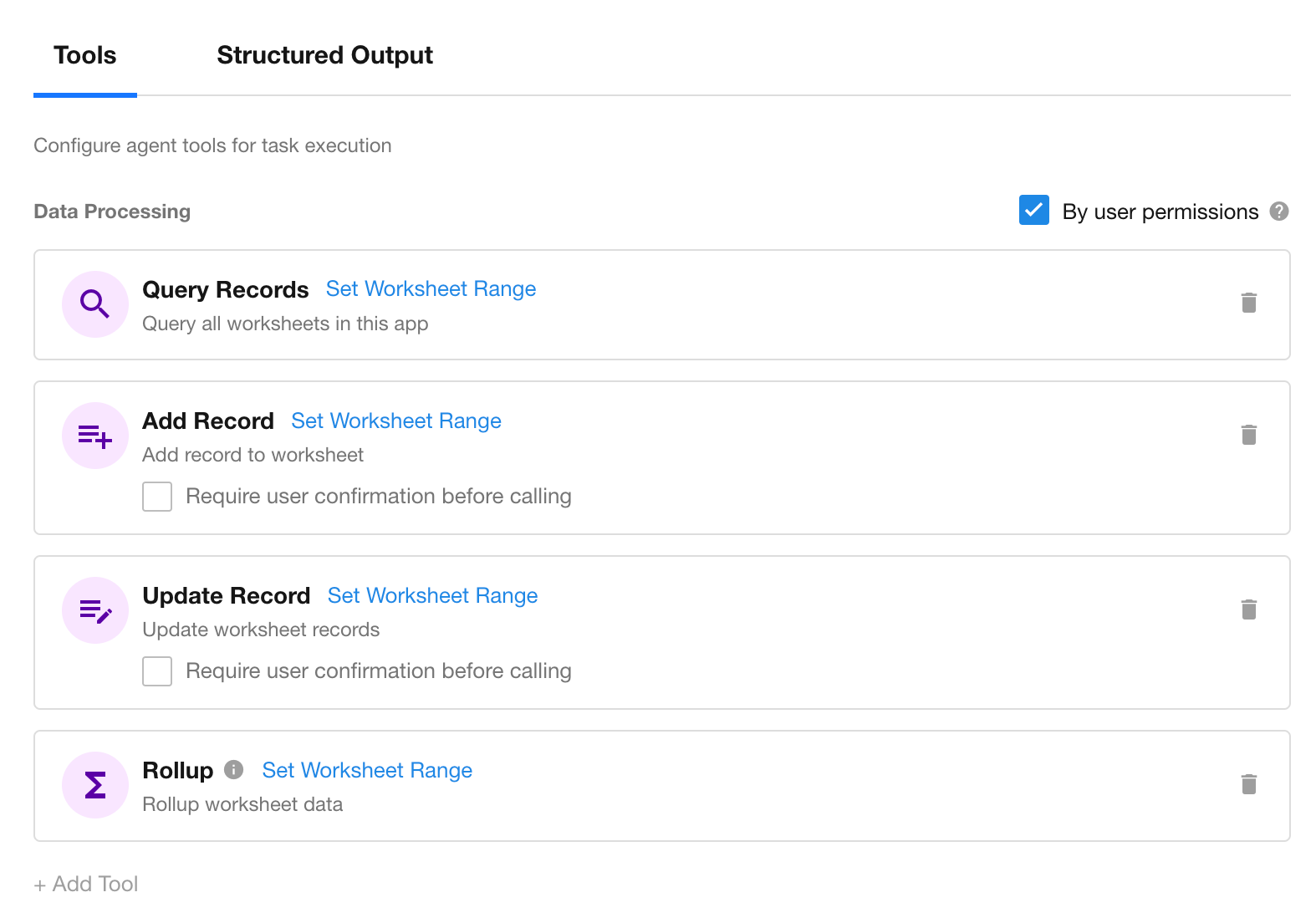
Tool Types
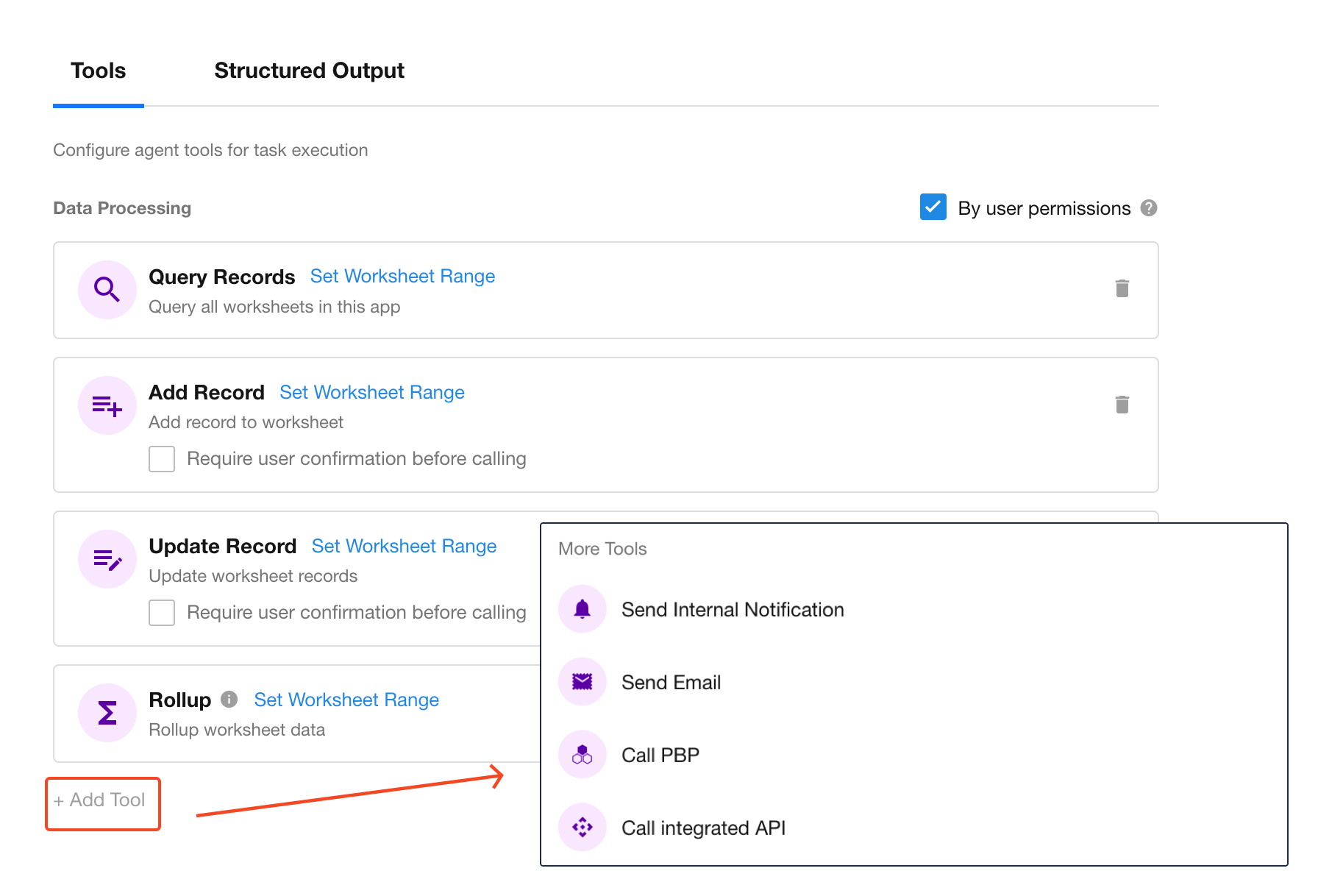
AI Agent nodes support four categories of tools. Click "+ Add Tool" to configure them.
-
Data Handling Tools
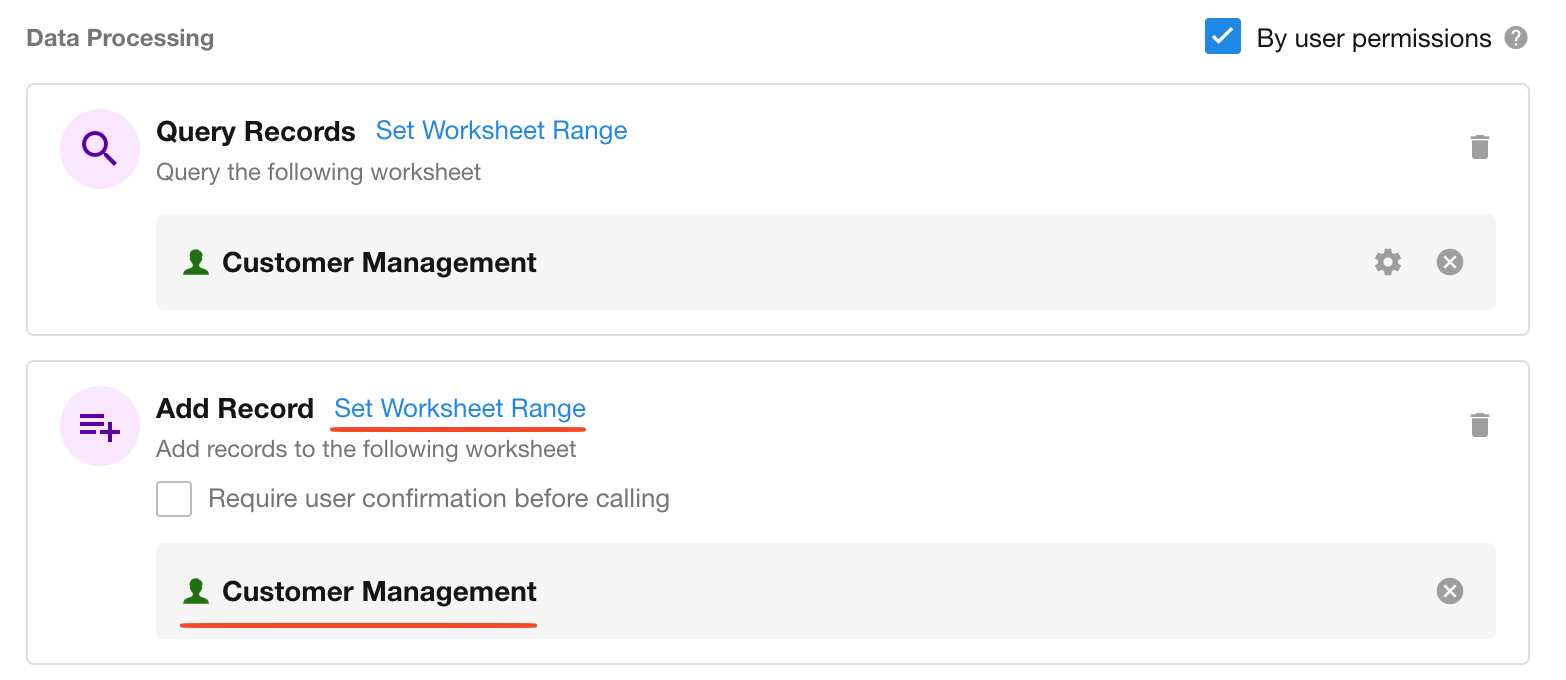
Includes “Query Records,” “Add Record,” “Update Record,” and “Rollup”.
tipRecord queries are executed through HAP’s API. Vector search (RAG) is currently not supported.
-
Notification Tools
Includes “Send Internal Notification” and “Send Email.”
-
Call PBP
Reuse logic by calling packaged business processes (PBP).
-
Call Integrated AP
Access external systems via APIs for cross-platform data retrieval or push.
Set Worksheet Scope
When using data handling tools, you can define the worksheet scope that the Agent is allowed to access.
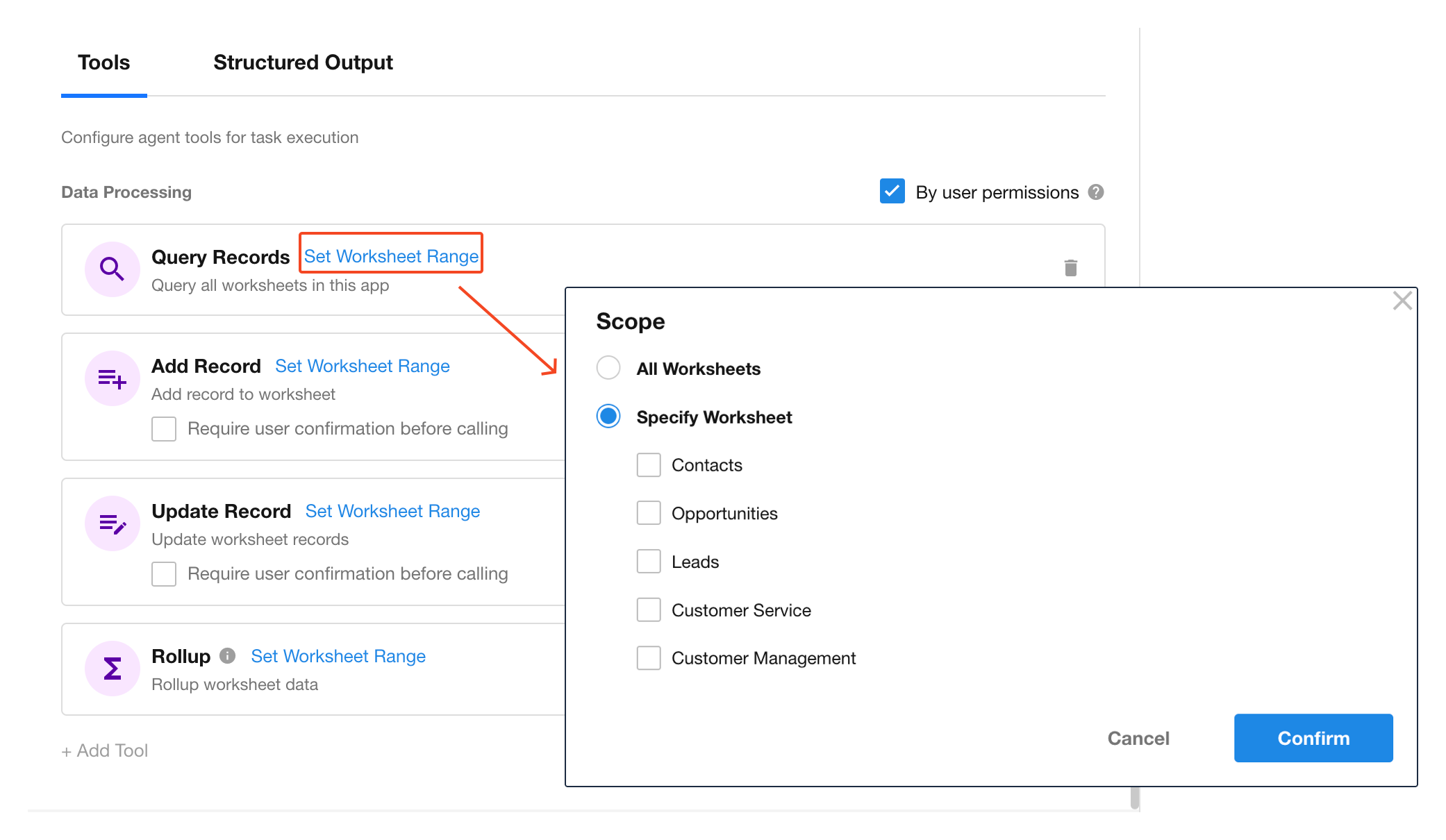
The system will automatically load all worksheets accessible within the current workflow. You may configure:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| All Worksheets | The Agent determines the target worksheet automatically based on context. |
| Specific Worksheets | Manually select target worksheets to limit access. This improves response time and reduces token usage. |
⚙️ Tip: In scenarios involving sensitive or multiple worksheets, it is strongly recommended to manually specify the worksheet to restrict the Agent’s data access.
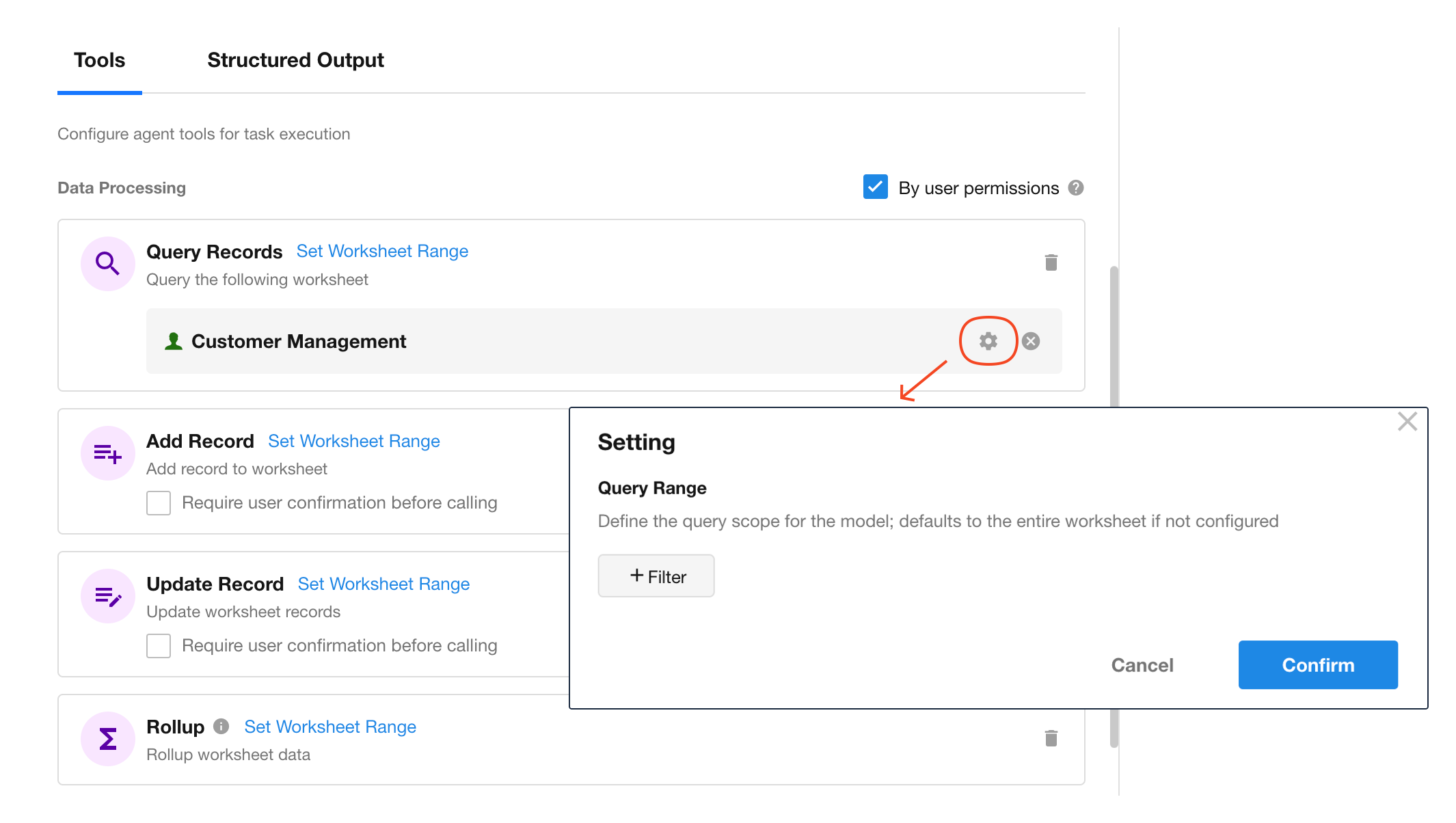
Query Filters
When using “Query Records” or “Rollup” tools, you can define additional filters to further constrain data access.
Set filter conditions to ensure access is limited to specific data segments, reducing risk of unauthorized access.
Example:
Set a filter like [Customer Status = High Value AND Last Follow-Up ≥ 7 Days]. The Agent will then only retrieve matching customer records when performing reminder tasks.
Output Configuration
After an AI Agent node finishes execution, it will generate output data that can be referenced by subsequent nodes as parameters.
The output includes three types of content: system fields, structured output parameters, and tool output parameters.
System Fields
By default, the AI Agent node returns the following system fields:
AI Generated ResultAI ModelToken Usage
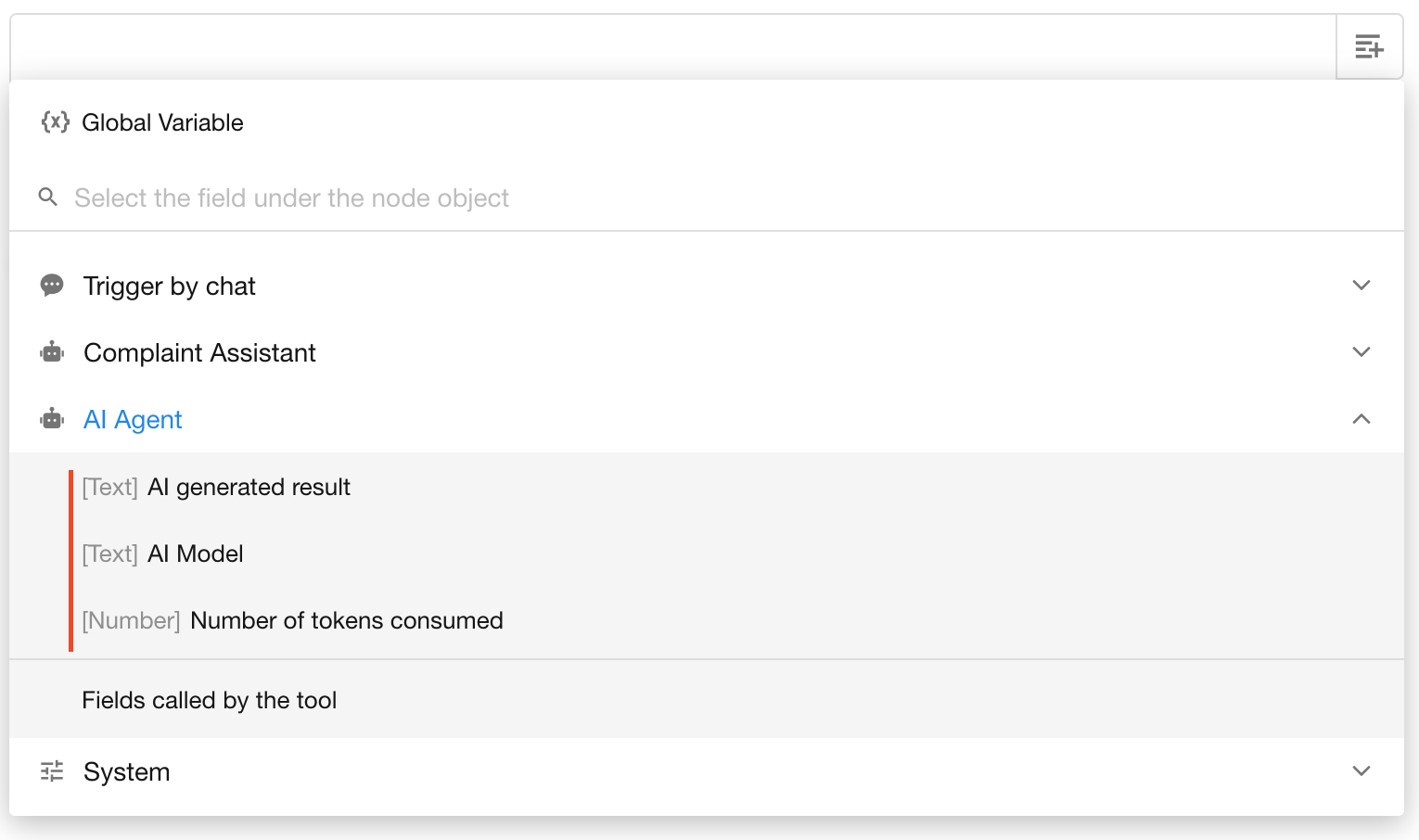
Worksheet Fields from Tool Invocation
When the AI Agent invokes tools like Query Records, Add Record, or Update Record, and a worksheet scope is defined, the fields from the affected records can be referenced by downstream nodes.
If multiple records are returned, only the first row will be taken by default.
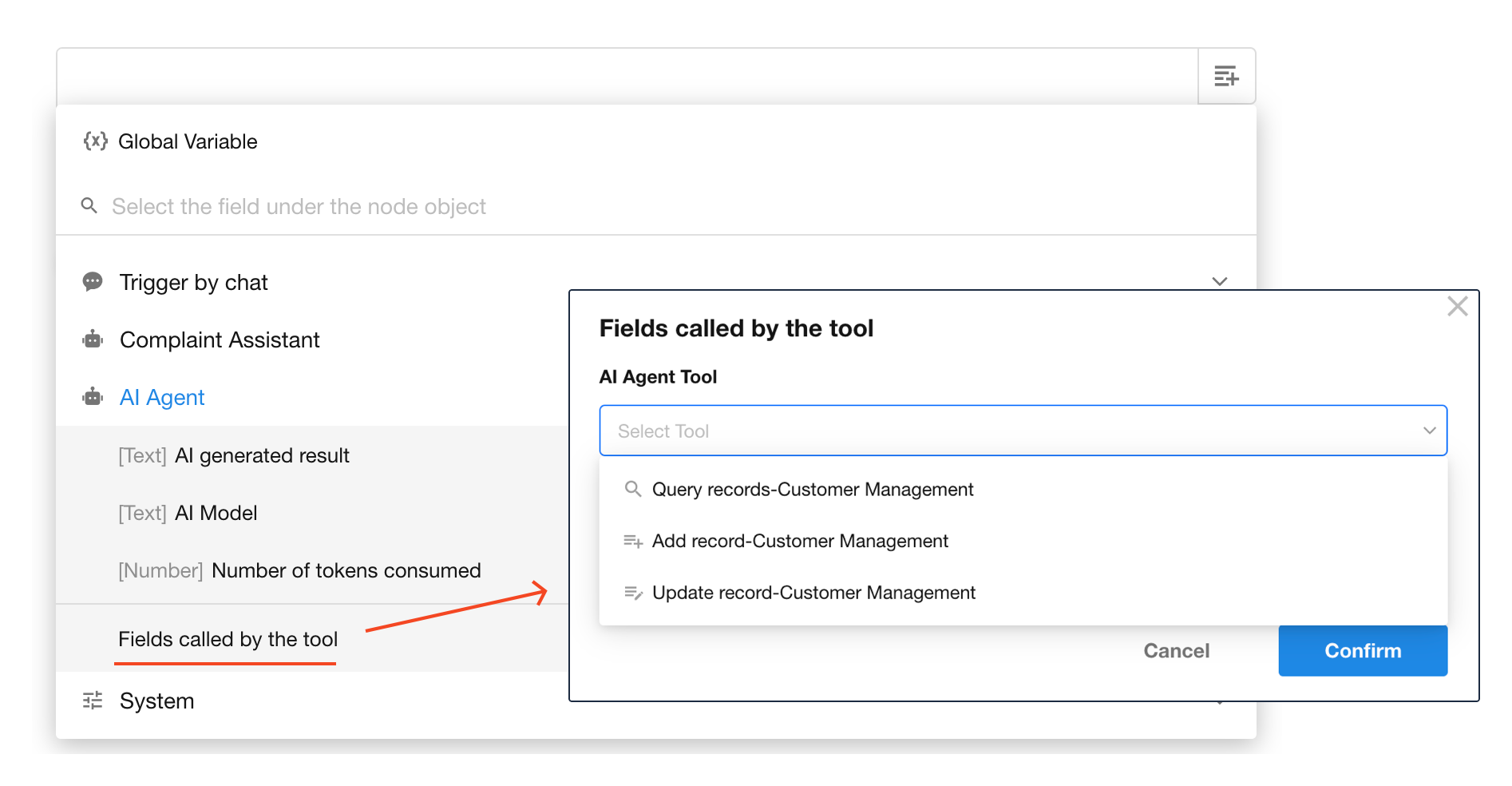
To use the output values in subsequent nodes, follow these steps:
In a downstream node (e.g., an AI-Generate Text node), expand AI Agent → Fields called by the tool, and select the desired field.
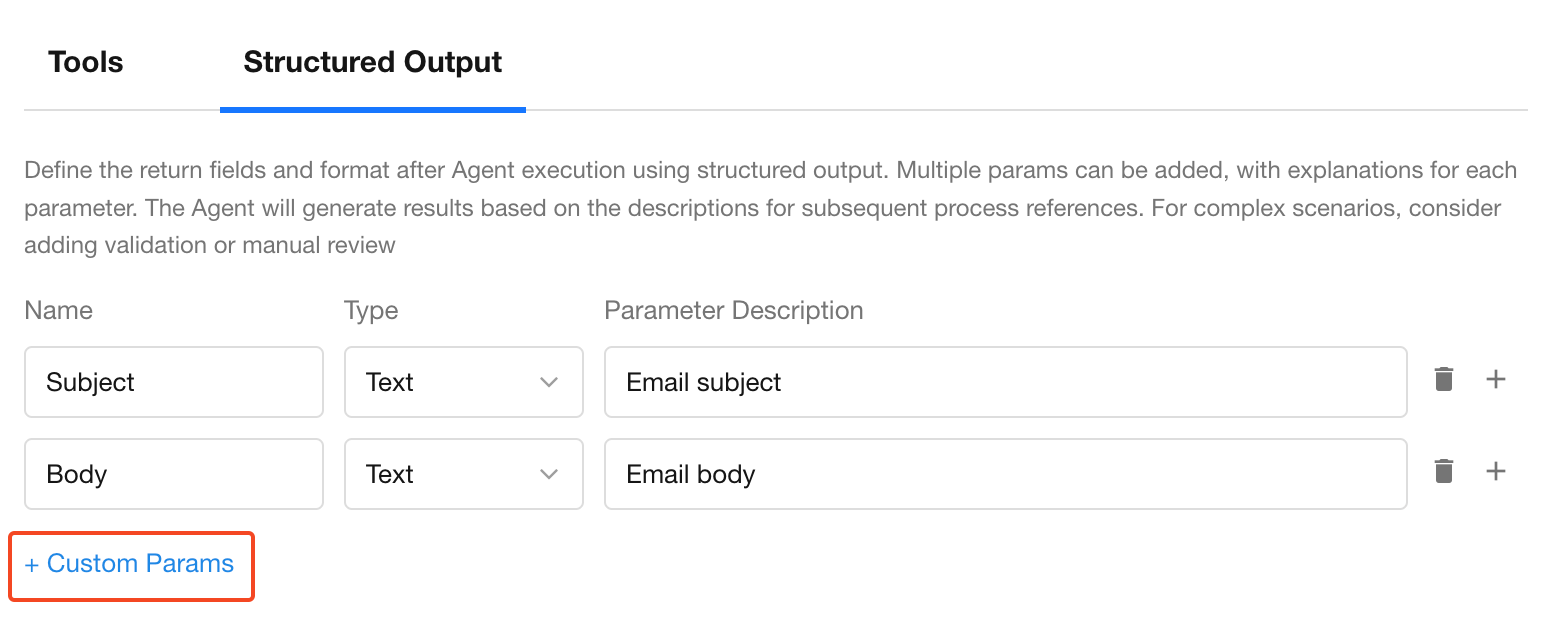
Structured Output
Structured output allows you to define custom fields and output formats. You can add multiple parameters and provide descriptions for each. The Agent will attempt to generate output that matches the format, which can be directly used in downstream workflow steps.
💡 The accuracy of structured outputs depends on the model’s comprehension. We recommend validating field formats during testing, especially in complex scenarios.
Example:
Extract the subject and body from an AI-generated reminder email.
Referencing in Subsequent Nodes
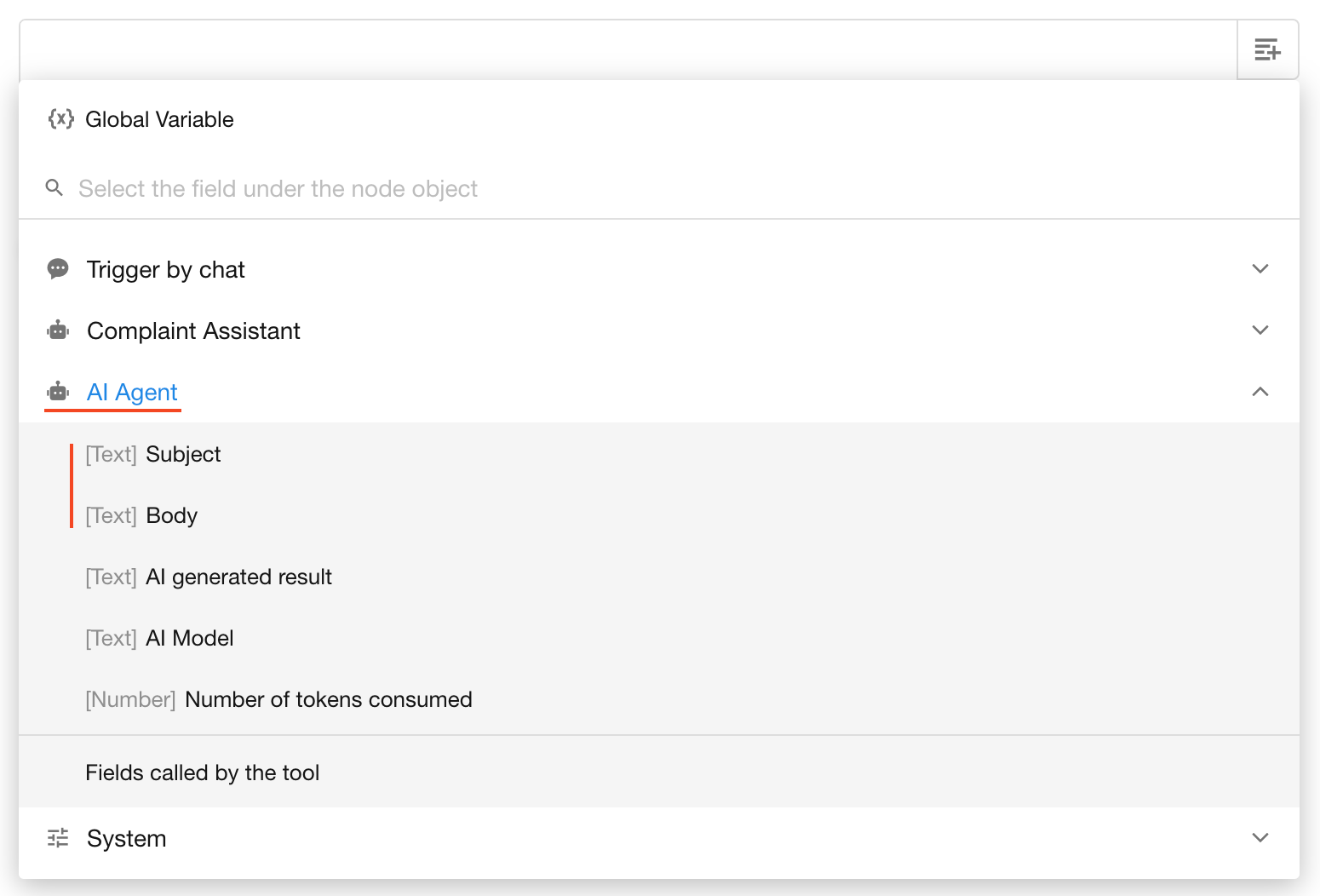
Agent Execution Logs
Each time an AI Agent node is executed, a detailed execution log is automatically generated. This log helps users inspect the model's runtime behavior and output.
How to View Logs
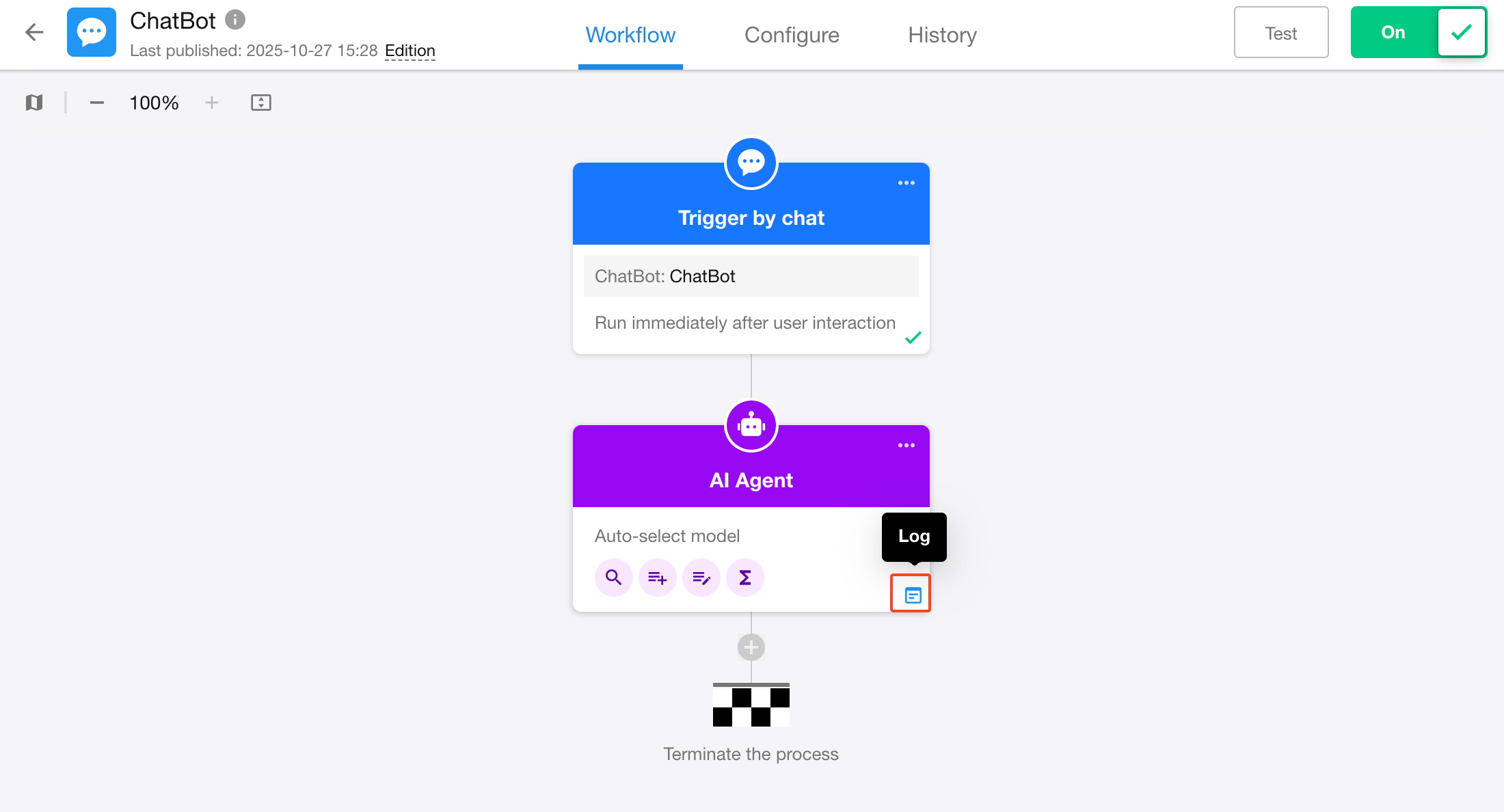
Method 1: During Test Run
Click the Test button in the top-right corner of the workflow editor. The system will execute the workflow step-by-step starting from the trigger node.
When execution reaches the AI Agent node, you will see its status (Running / Success / Failed) on the canvas.
Hover over the node and click the Log button to view details.
Method 2: From Workflow Execution History
Go to the workflow’s execution history page and click View Details inside the AI Agent node.
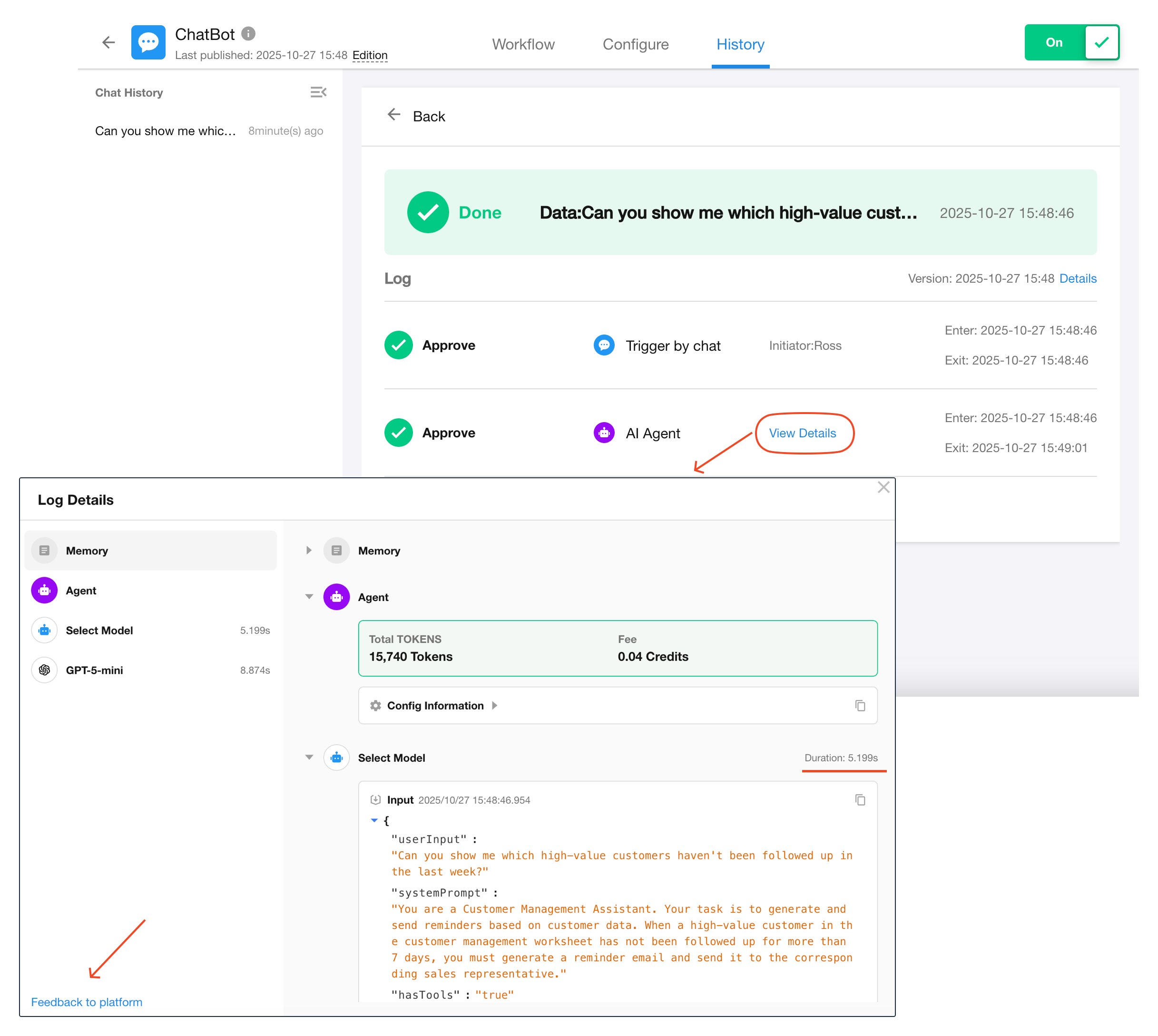
Log Structure
The log is split into two sections:
- Left Panel: Lists execution steps (Memory, Agent, Model, Tool) in sequential order.
- Right Panel: Shows detailed input/output of each step.
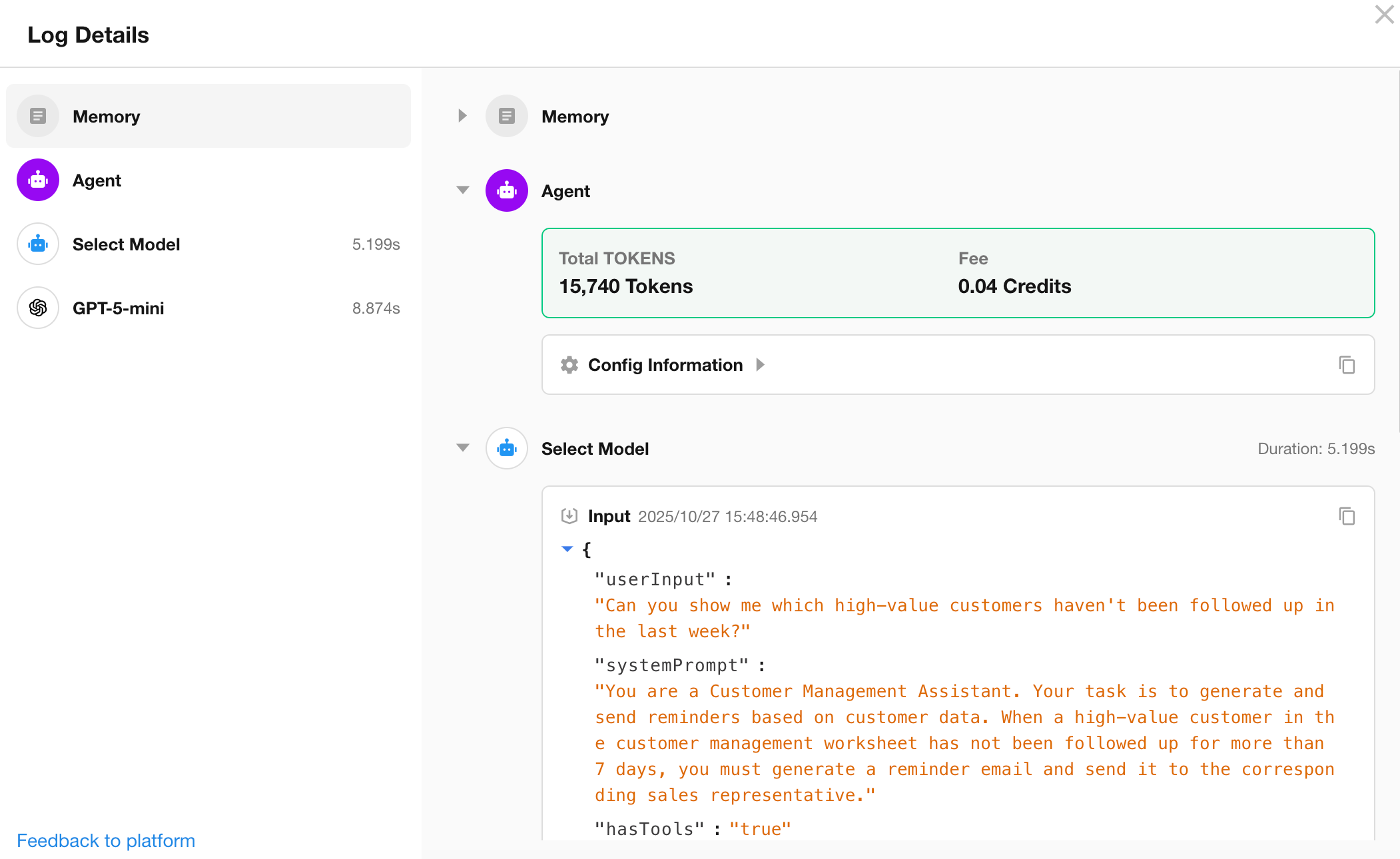
Step types include:
-
Memory: Stores conversation history, including user inputs and Agent responses (only in ChatBot workflows).
-
Agent: Records configuration details of the node.
-
File Parsing: Displays file parsing process and results.
-
Model Selection: If “Auto-select Model” is used, logs the request and selected model.
-
Model: Logs input/output of the language model, including any tool calls.
-
Tool: Logs tool execution details such as input parameters and response results.
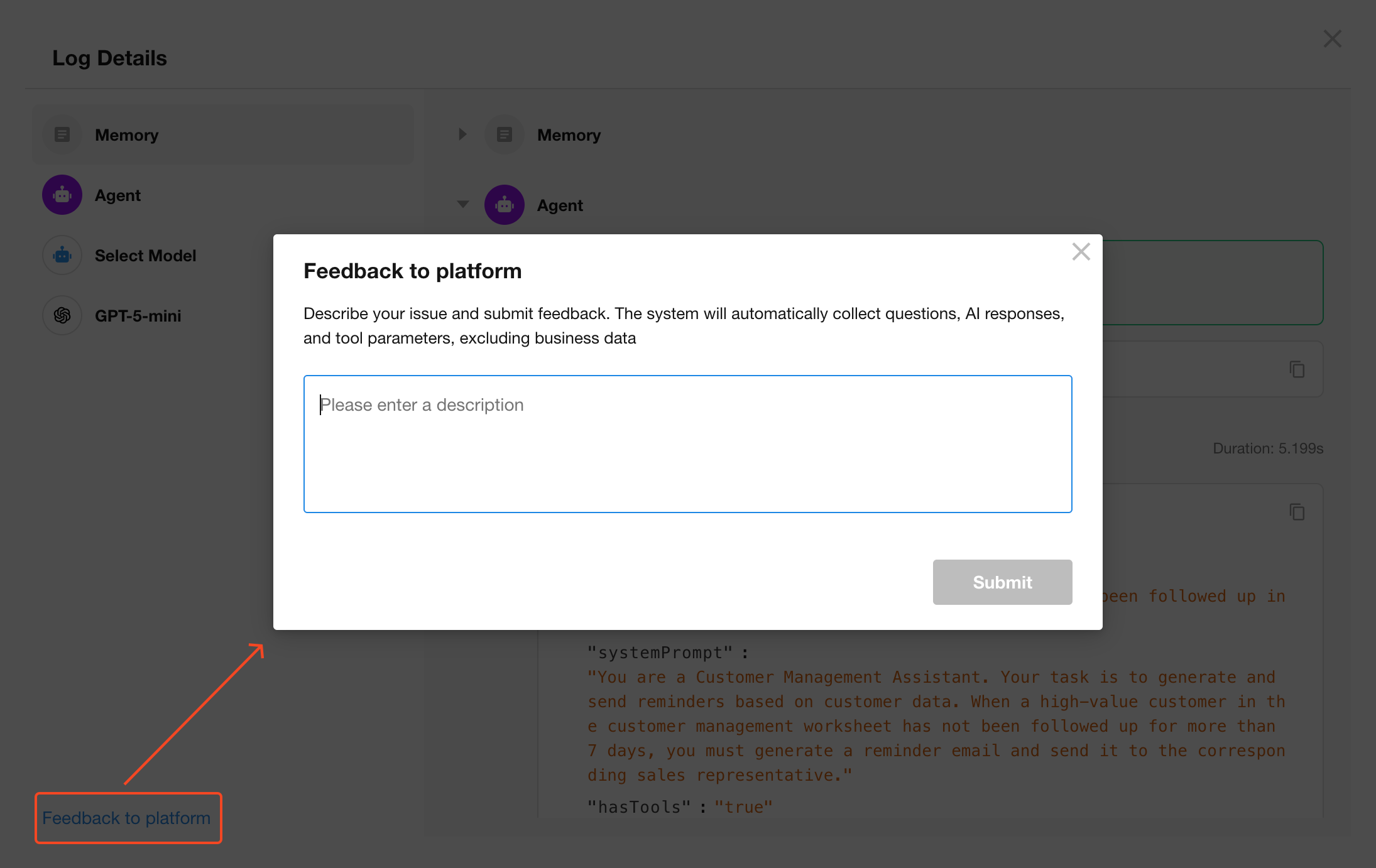
Submitting Feedback to HAP
If you encounter issues or have questions about an AI Agent’s behavior, click Feedback to Platform at the bottom-left corner of the log viewer.
🔒 Only the prompt, AI response, and tool parameters are submitted. No business data is collected.
5. Cost Overview
You can view token consumption and associated costs for each Agent node directly in the execution logs.
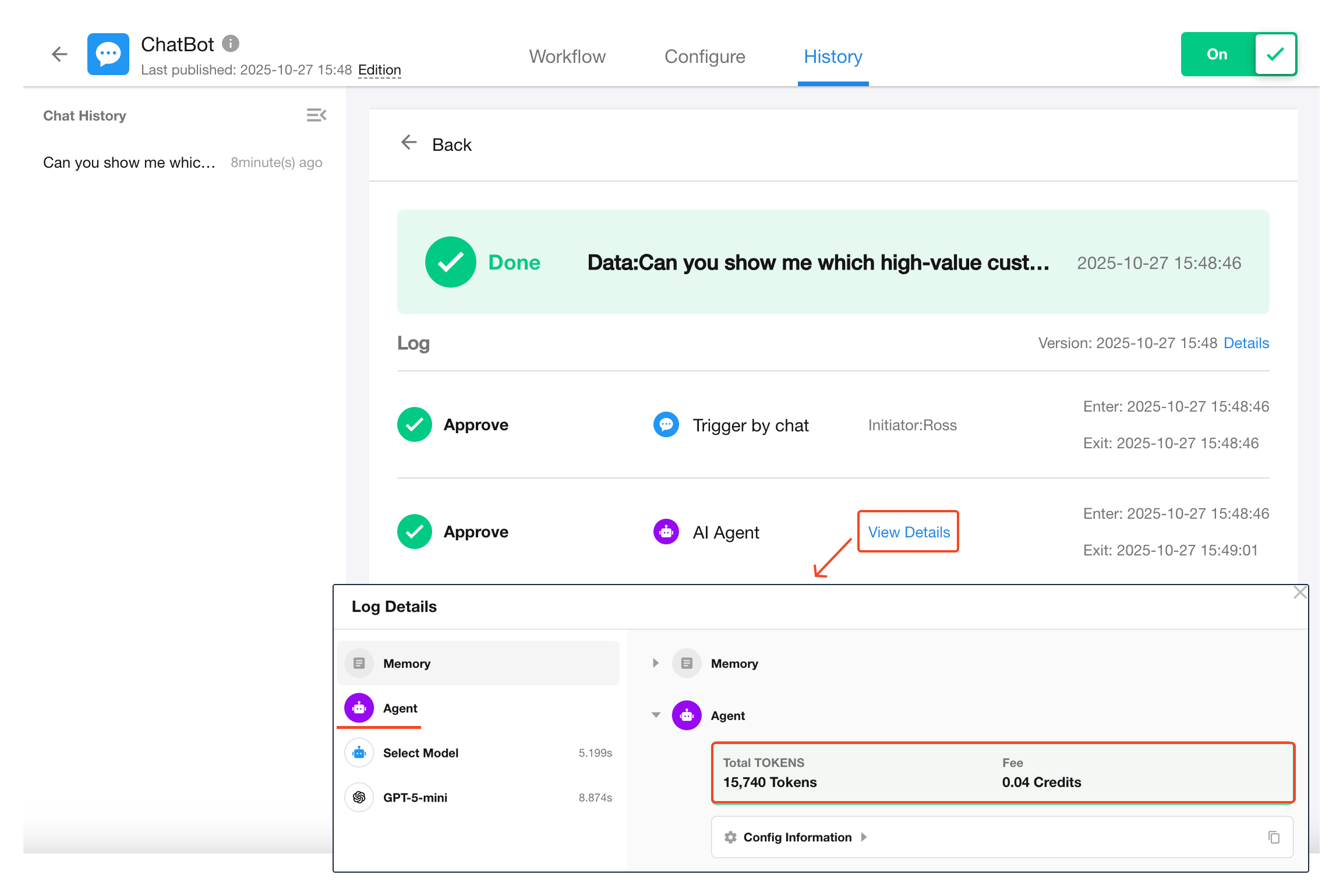
Each AI Agent node consumes tokens from a selected large language model. Costs are deducted from the organization’s credit balance based on model pricing.
1 credit = ¥1 RMB