Introduction to Workflow
Overview
Every business operation follows a set of processes consisting of a series of activities (which can be broken down into tasks). These activities are interconnected through logical sequences or causal relationships, ultimately delivering an output to internal teams or external customers—such as product development processes or manufacturing workflows.
Beyond operational processes, there are also approval workflows designed to mitigate risks, such as procurement approvals or leave request approvals.
Workflows provide an automated execution model for both business and approval processes. By analyzing and decomposing activities within a process, workflows define tasks, roles, and rules to enable automated execution and monitoring. This automation replaces repetitive manual tasks, reduces human intervention, and enhances operational efficiency.
Components of Workflows
A workflow consists of a trigger and multiple action nodes. The trigger serves as the switch for the workflow, while various types of action nodes perform tasks to achieve process automation.
A simple workflow model:
When a new ticket is submitted, assign it to different responsible parties based on the issue type.
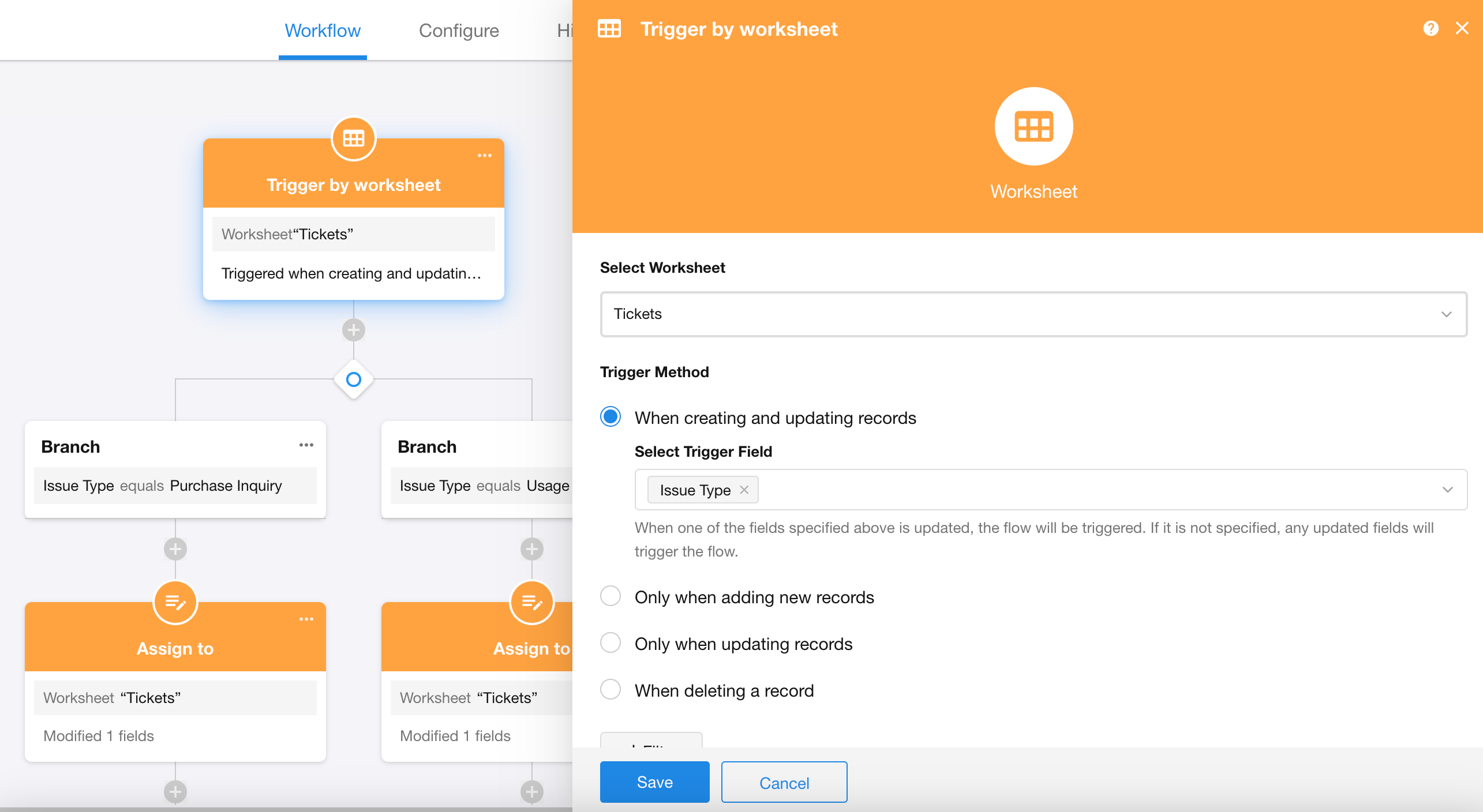
Trigger: When a ticket is created or modified
Automated Action 1 (Logical Branch): Two branches: "Purchase Inquiry" and "Usage Inquiry"
Automated Action 2 (Update Record): Corresponding operations under each branch: Modify the "Responsible Person" field
Characteristics of Workflows
Workflows are a new type of business process management (BPM) tool that differ from traditional BPM in the following ways:
-
Completely internet-based - Can connect to external data sources
-
More user-friendly creation and maintenance - No advanced IT knowledge required
-
Emphasizes automated triggering and execution
Workflows can help solve the following informatization challenges::
-
Automated data processing
-
When data changes meet set conditions, create or modify data in other worksheets
-
When scheduled times are reached, modify certain record data
-
-
Business process approvals
-
Business approvals like sales orders, project changes
-
Administrative approvals like leave requests, item requisitions
-
-
Notifying internal/external personnel to view or fill in data
-
Notify internal members of data changes via system messages for viewing/modification
-
Send record content to external users via email/SMS for viewing/modification
-
-
Data integration with external systems
-
Push worksheet data to external systems
-
Proactively or passively retrieve data from external systems to write/update worksheets
-