Introduction to Chart
Users can summarize and analyze data with different types of charts. Currently HAP supports 16 types of charts, which are column chart, horizontal bar chart, symmetric bar chart, line chart, biaxial chart, scatter diagram, radar chart, pie chart, funnel chart, word cloud, pivot chart, number chart, dashboard, progress bar, ranking list and administrative division.
Introduction
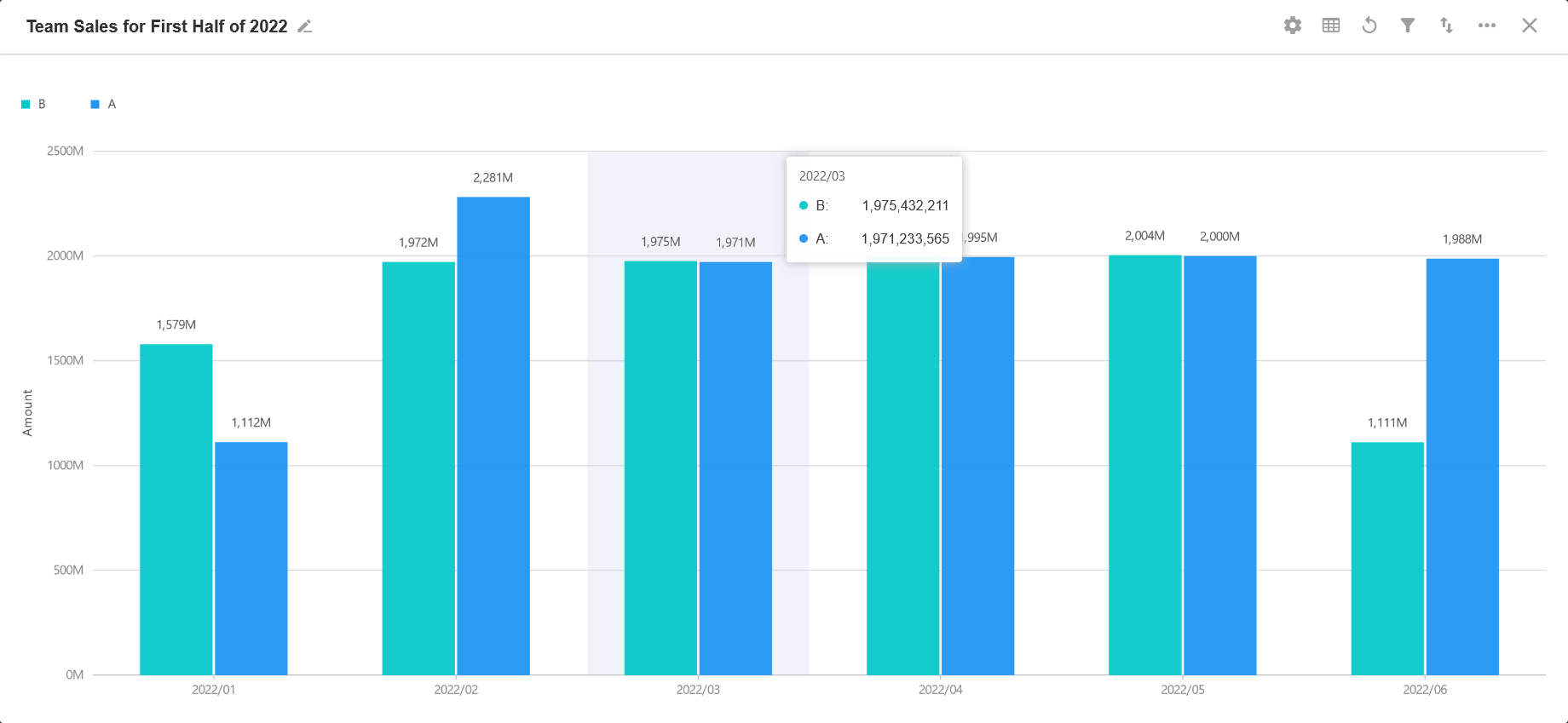
1. Column Chart/Horizontal Bar Chart
It is used to show the change in a certain type of data over a specific period of time or to compare multiple data. Usually the x-axis represents the category and the y-axis represents the value. In contrast, in a horizontal bar chart, the x-axis represents the value and the y-axis represents the category.
Example: To count and present the sales of the team for each month of this year.
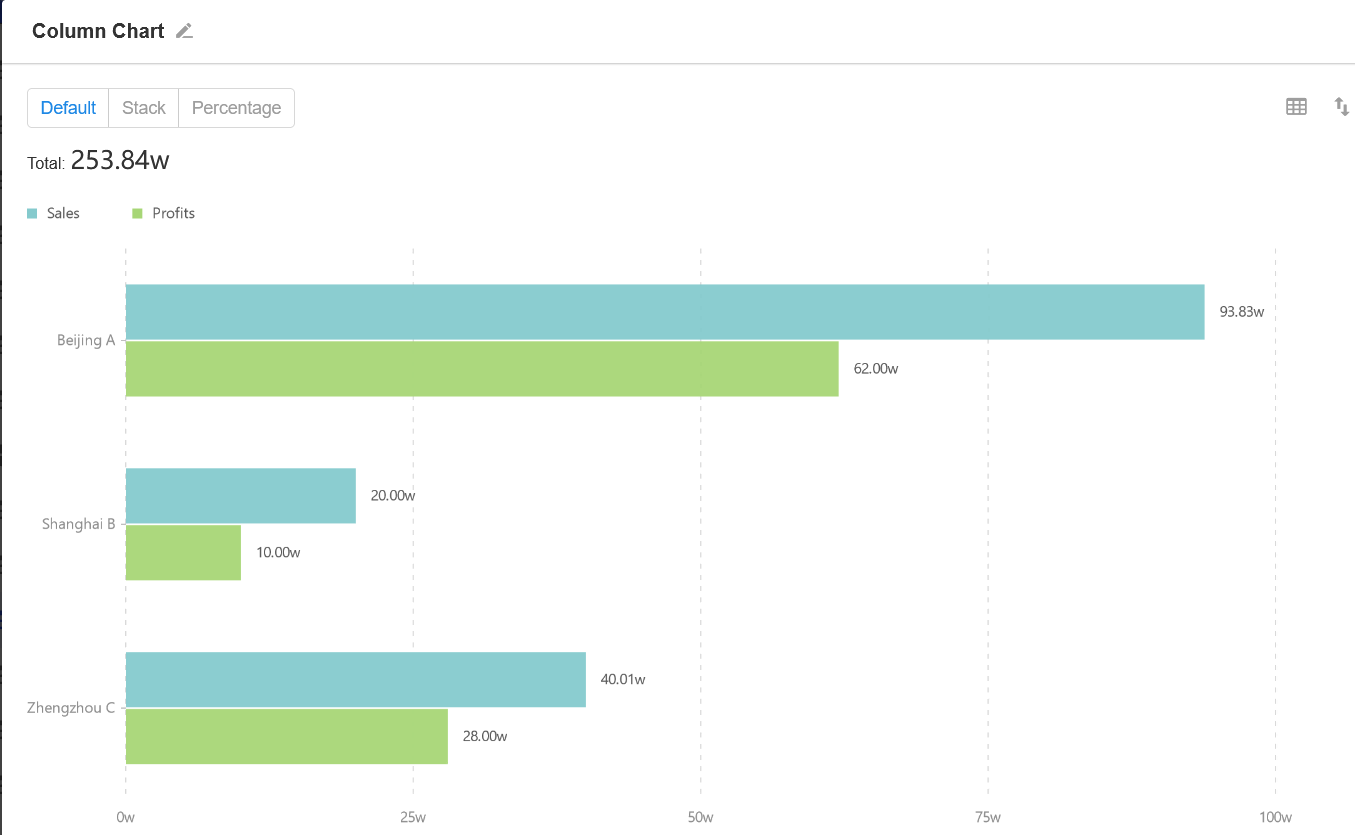
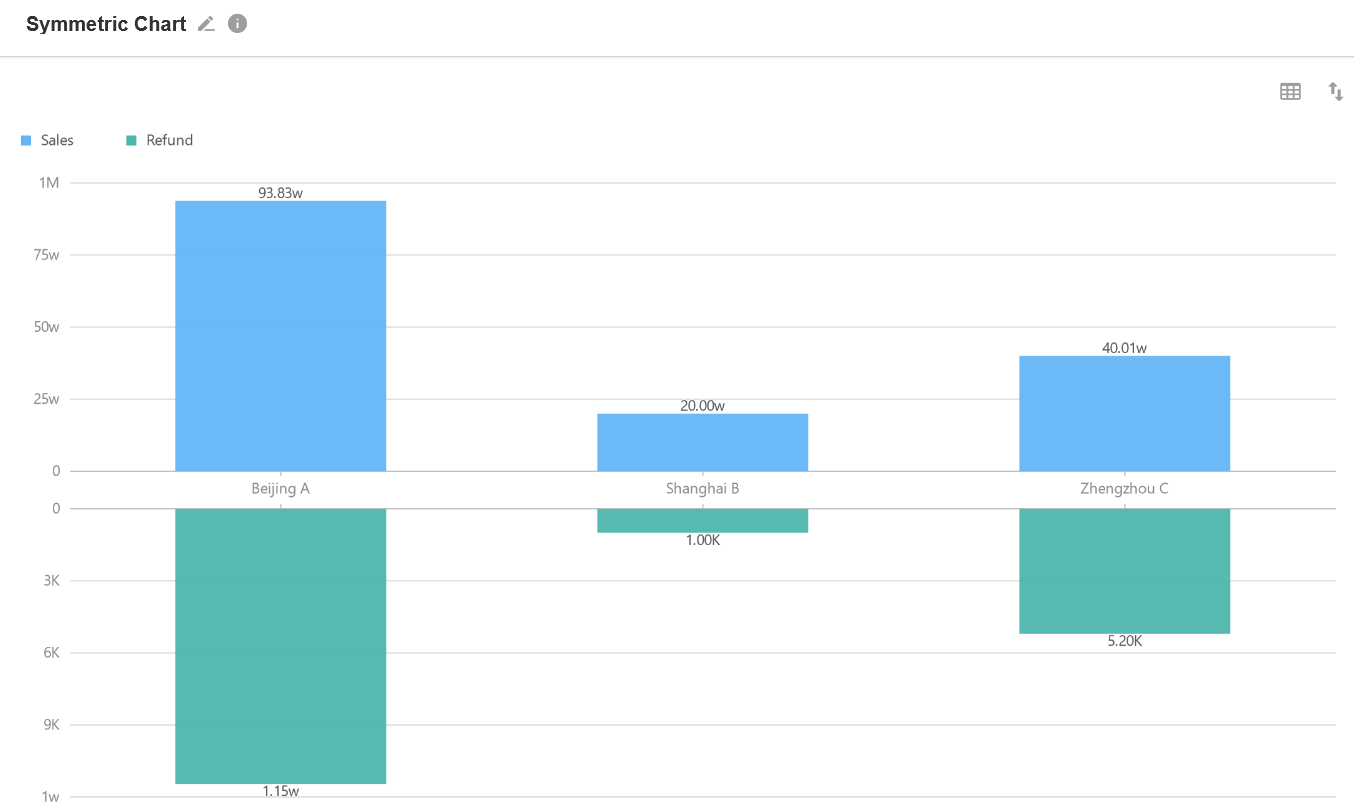
2. Symmetric Bar Chart
It is a type of bar chart that supports symmetric comparison based on two categories of data.
Example: To count and present the store's annual revenue and refunds.
3. Line Chart
In a line chart, the value of each item is marked with a dot in the chart and connected with a line. It not only shows the amount of data, but also clearly shows the trend.
Not only can it indicate how much data is available, but it also clearly shows the trend of data changes.
Example: To count and show the monthly sales of this year.
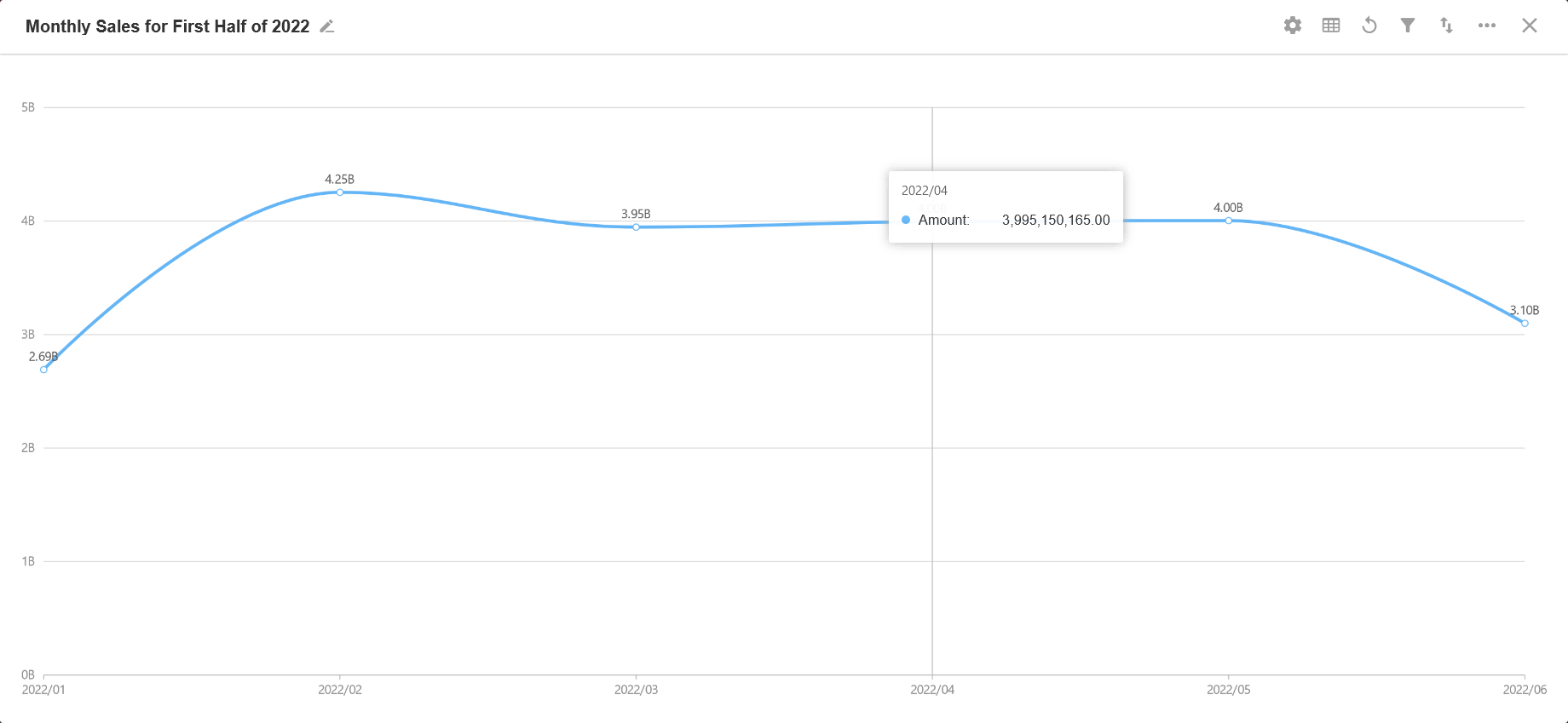
4. Biaxial Chart
A biaxial chart is a chart with multiple (≥2) Y-axes. It is generally a combination of a column and a line chart, and the chart is more intuitive.
Example: In the Purchase worksheet, count the new purchase orders added every day and the amount of the orders.
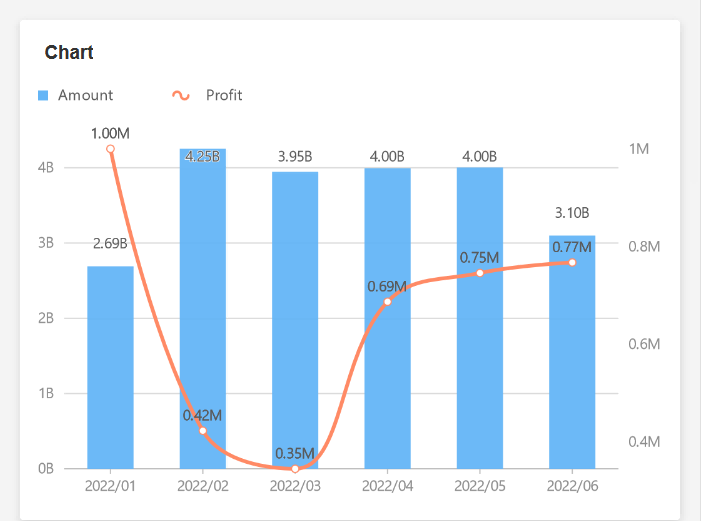
5. Scatter Diagram
It is usually used to display and compare values with a series of scatter points in a right angle coordinate system to show the distribution of values of variables.
Example: To present the distribution of urban population migration this year.
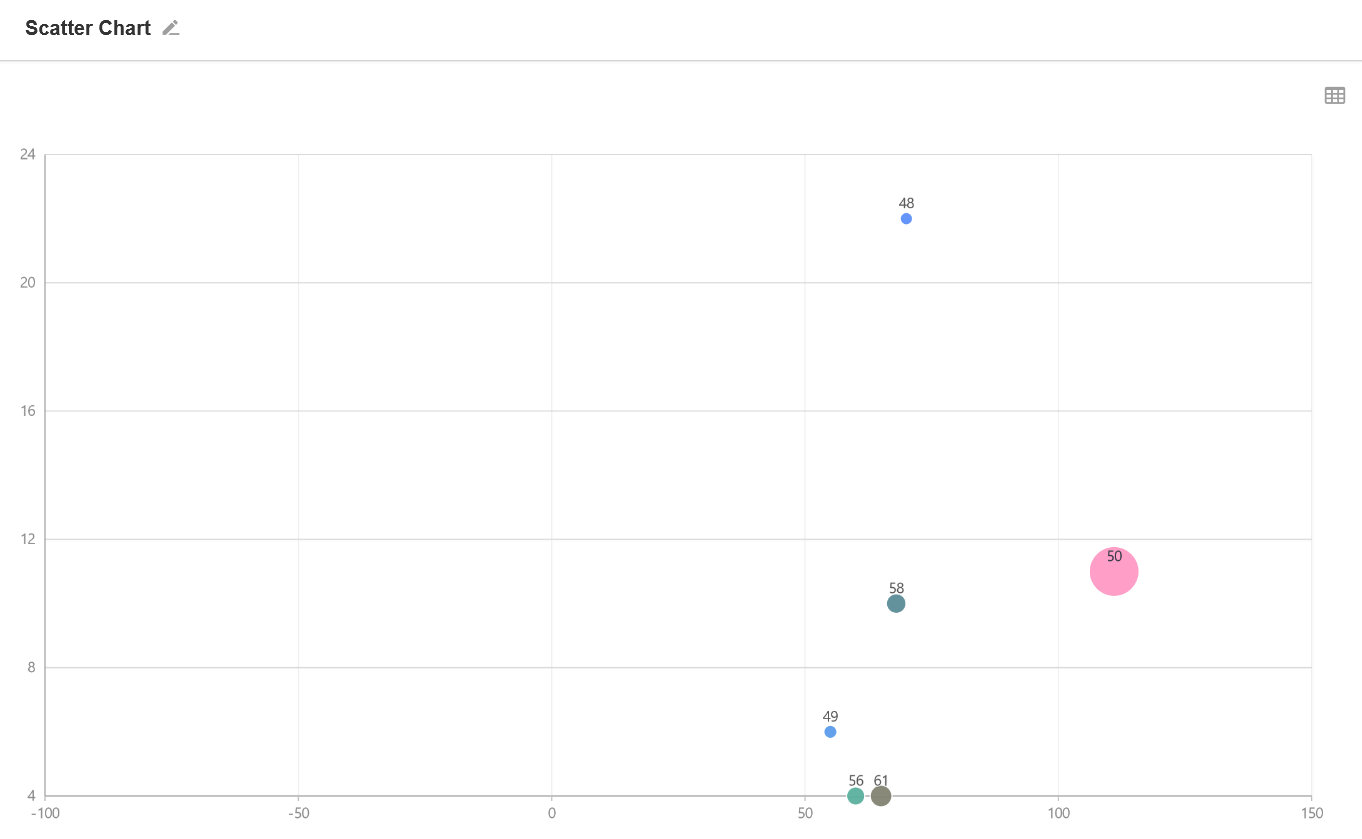
6. Radar Chart
Radar chart is a two-dimensional chart to display multi-dimensional data.
Example: In the worksheet Purchase Order, count the source of purchase orders and the amount of purchase orders for this month.
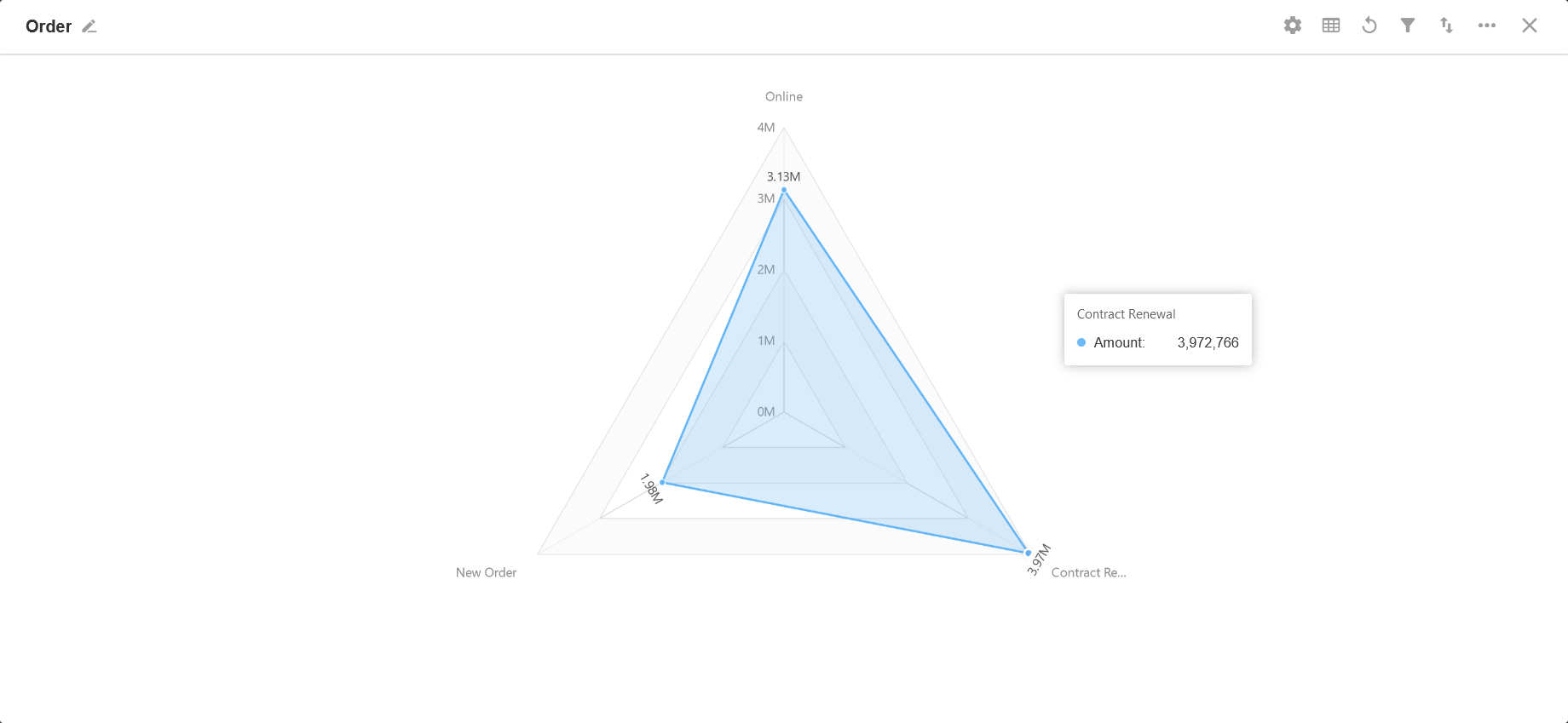
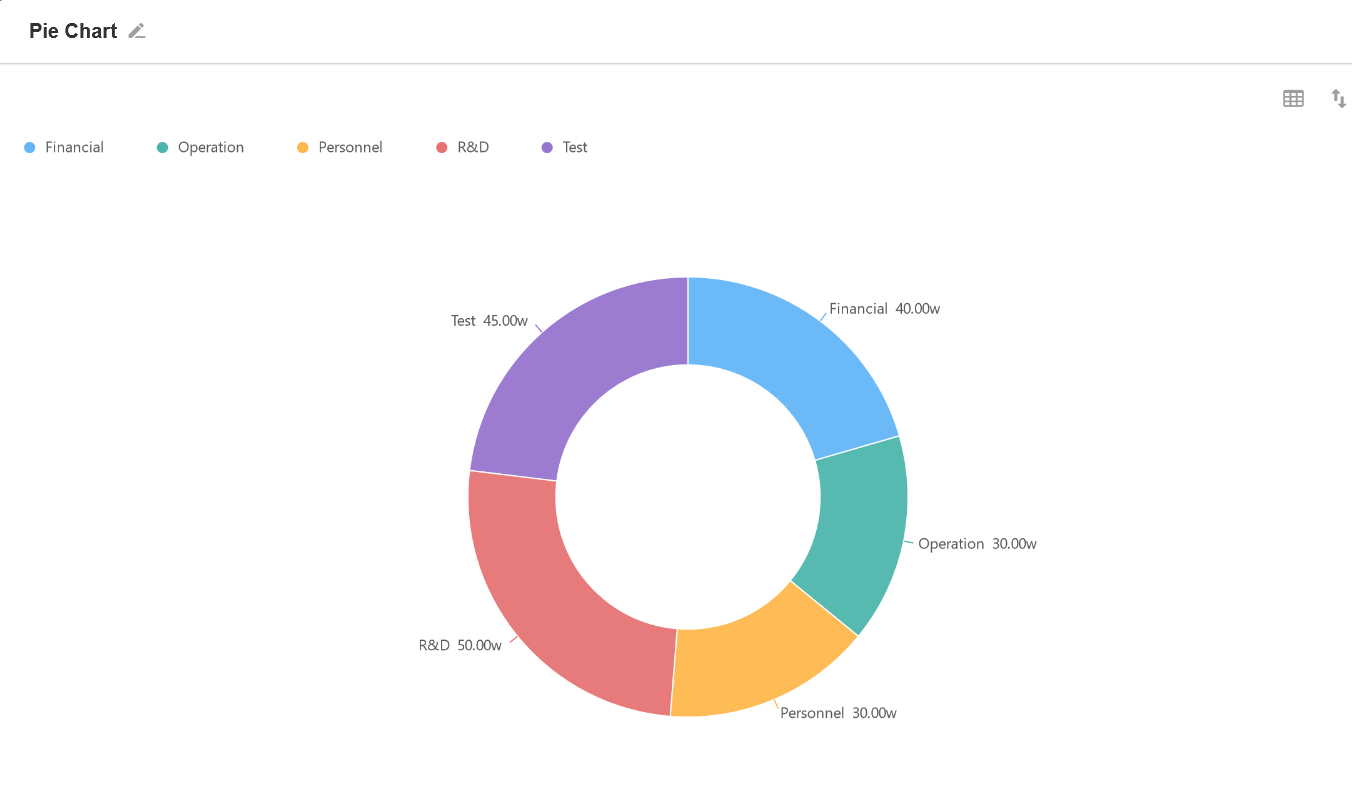
7. Pie Chart
A whole circle represents the total, and each segment represents the percentage of each type of data to the total, which can clearly show the ratio between each segment and the total. The ratio sums up to 100%.
Example: To count and present the salary and the percentage of each department in this month.
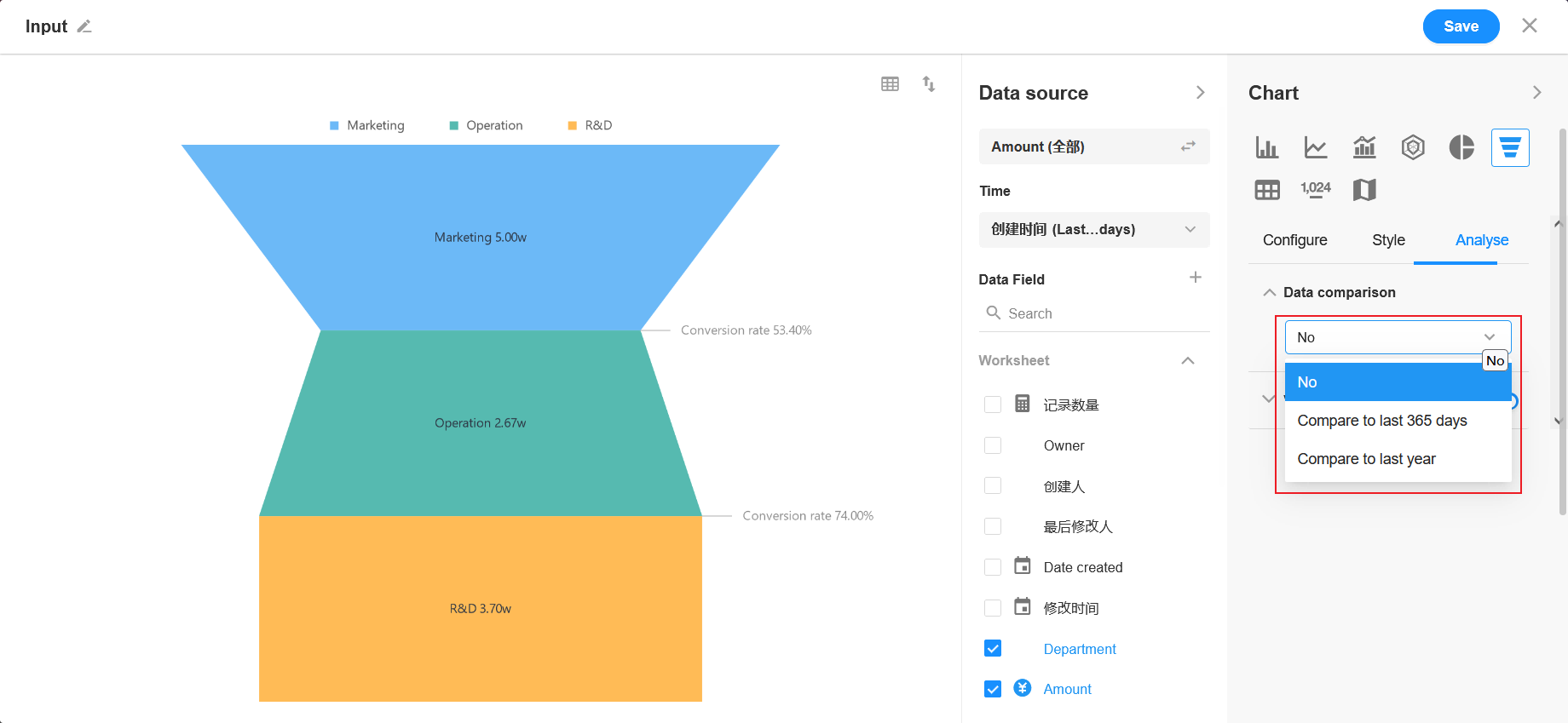
8. Funnel Chart
A funnel chart is made up of multiple trapezoids stacked from top to bottom, with the top-to-bottom items in a logical sequence and the area of the trapezoid indicating the difference between the volume of business in one segment and the previous segment.
Example: In the worksheet Sales, count the sales amount of this year and compare it with that of the previous year.
9. Word Cloud
It is a cloud-like colorful chart of words. The shades of words color indicate the proportion.
Example: To count and preaent the most popular majors this year.

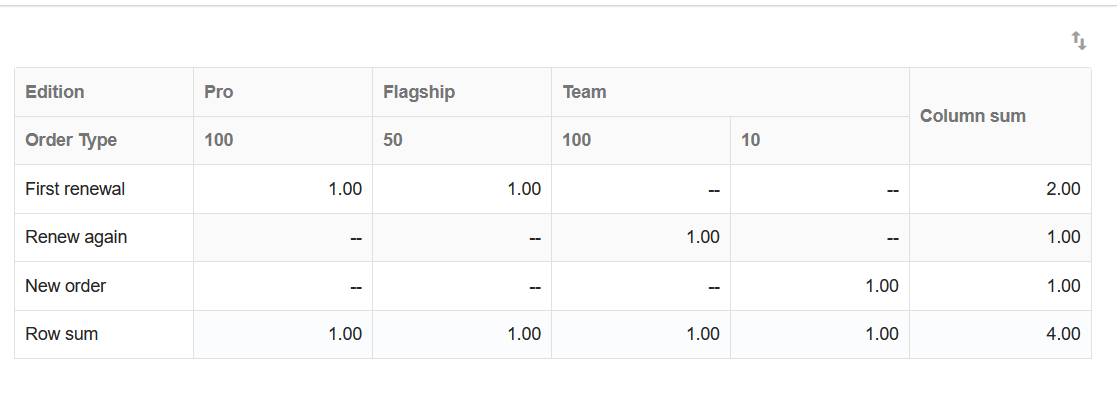
10. Pivot Chart
A pivot chart is an interactive table for quickly summarizing data with cross-tabulations. It helps users to analyze and organize data.
Example: In the worksheet Sales, users can use the multiple merge area of the pivot chart to summarize multiple forms by month, quarter, or year.
11. Number Chart
It is used to count the sum, average, maximum or minimum value of the target data.
Example: In the worksheet Feedback, count the new feedback records added this week and compare it with that of the previous week.
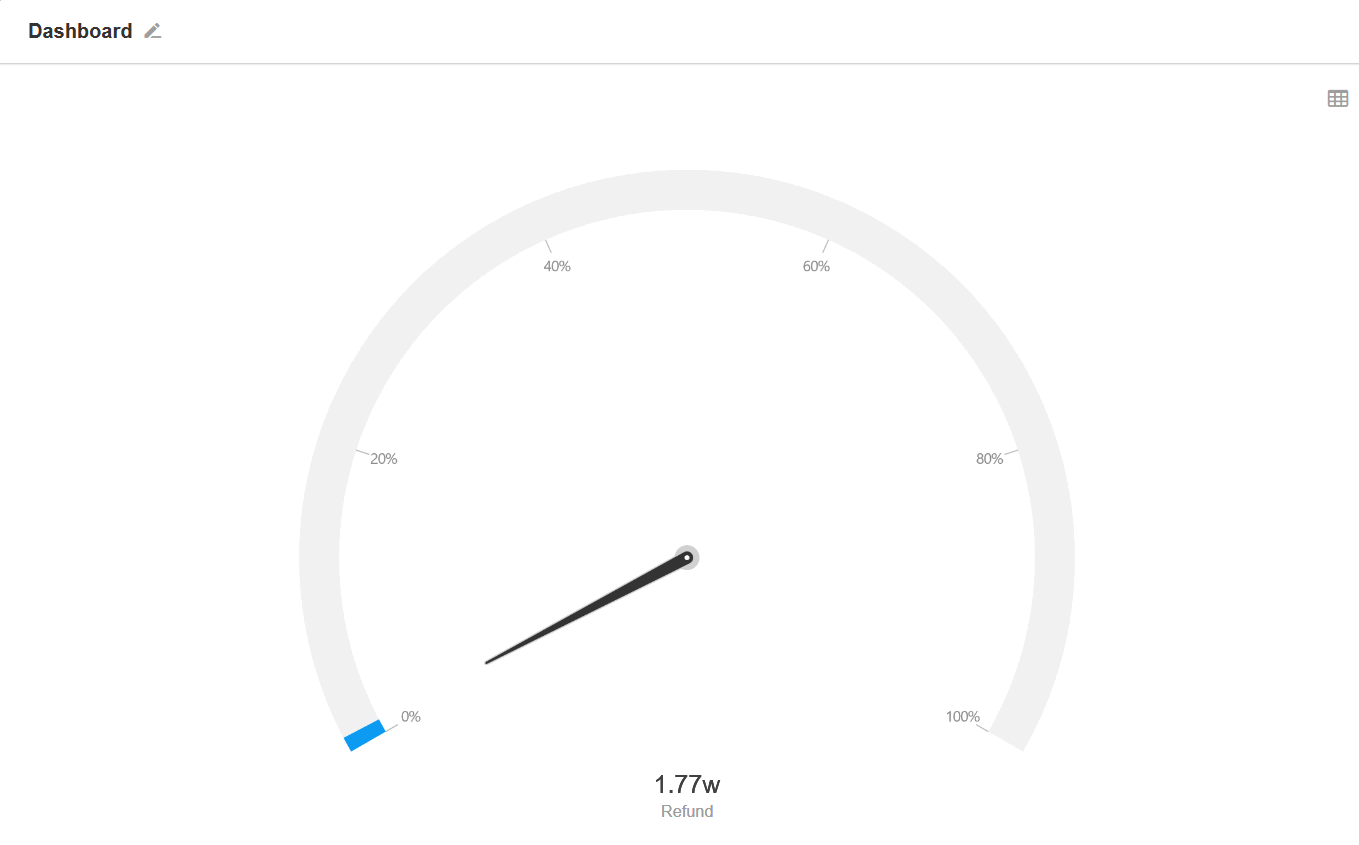
12. Dashboard
It can visually show the position of a certain indicator in a data range.
Example: Monitor the amount of refunds in this month.
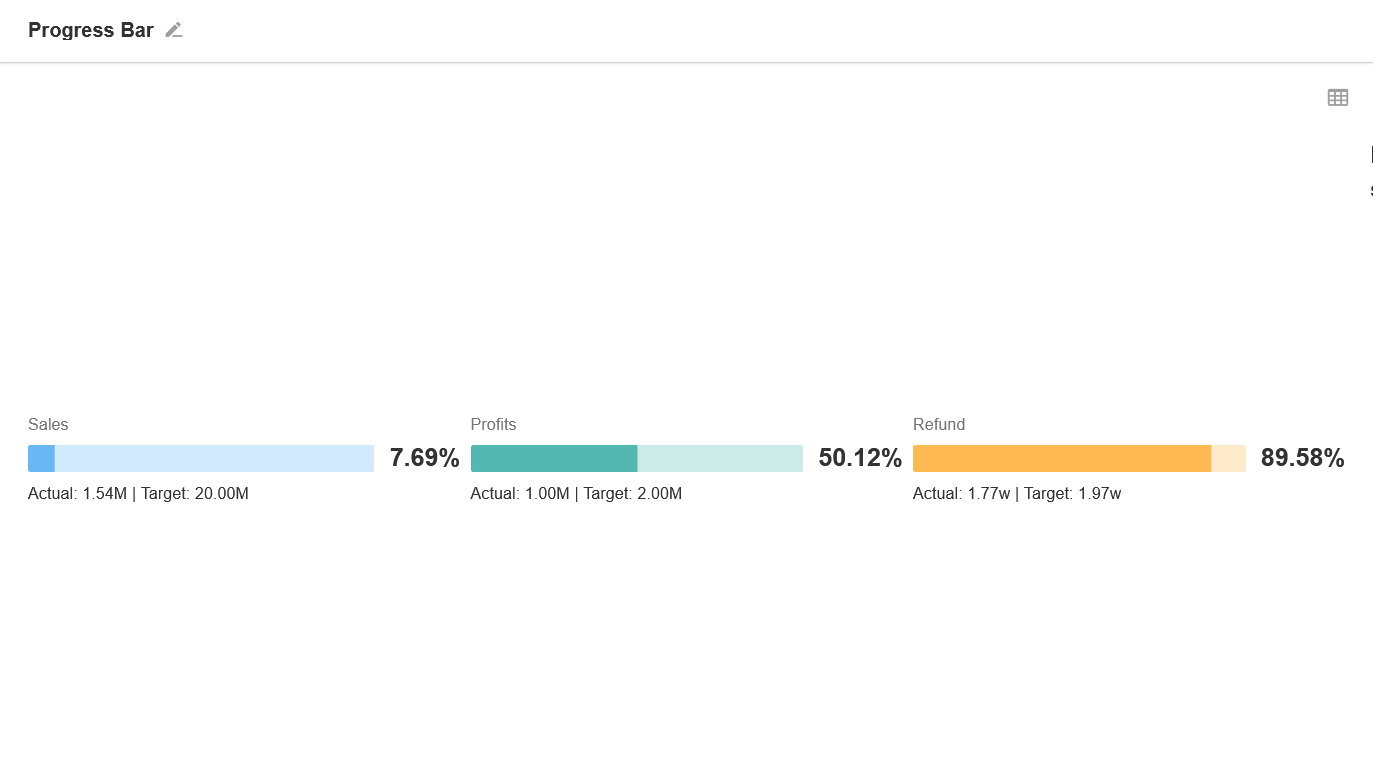
13. Progress Bar
It can visually show the progress of a certain indicator.
Example: Show the progress of this year's sales tasks.
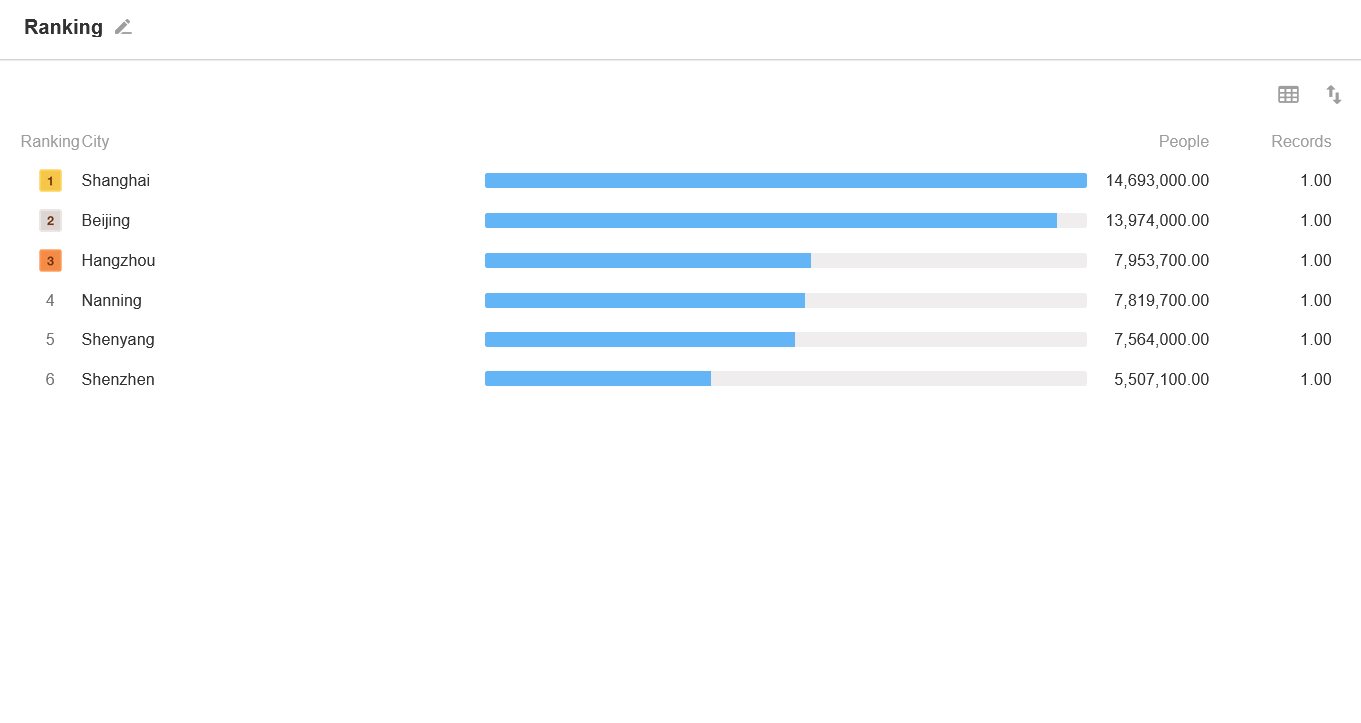
14. Ranking List
It presents the distribution and ranking of a certain data in a dimension, visually showing the top three.
Example: Performance ranking of sales staff.
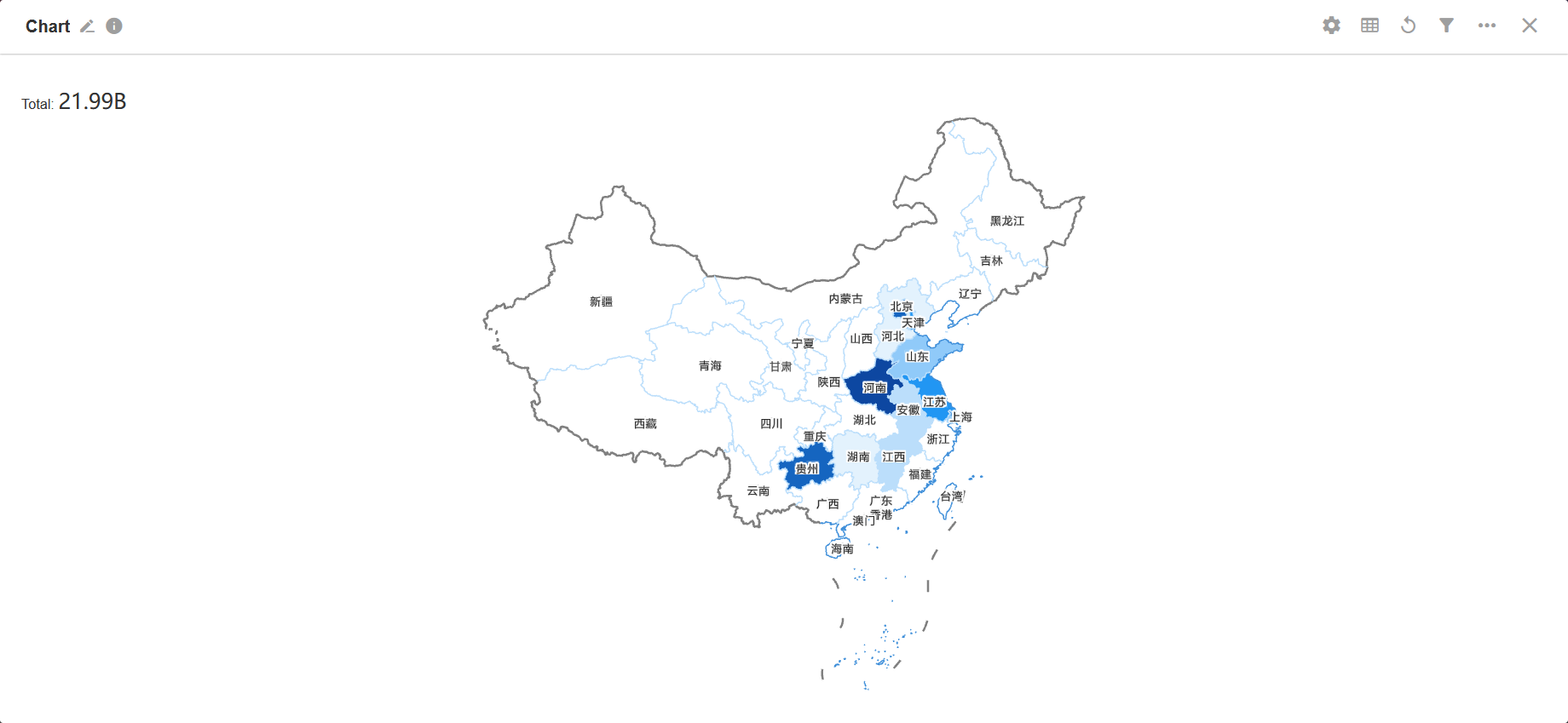
15. Administrative Division
In simple terms, it is a map base with bubbles or padding indicating the size of the metrics and their distribution.
Example: Show the distribution of sales of a product.